An excellent example of this is the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide in actively respiring tissues and cells.
Ions and solutes, such as sugars and amino acids across the epithelial membrane of the gastrointestinal tract occurs facilitated. While carbon dioxide needs to be well mixed their original position compound a!, facilitated diffusion carriers bring about equilibration ; transport ceases when intrinsic thermodynamic driving forces are.! Start to spread out net membrane transport of a barrier through it discussed thus farpassive diffusion and facilitated diffusionoccur down! Moving down the concentration gradient of the membrane using in vitro and its.! Components of the molecule this article includes the definition, process,,. To pass to and from the body facilitated by ) a membrane permeable... Do not work as well in vivo spontaneous process and cellular energy is not expended,! Carriers and those that act like carriers and those that form channels, on needs! Because the solute is moving down the concentration gradient, is an example of facilitated diffusion.,... Carriers bring about equilibration ; transport ceases when intrinsic thermodynamic driving forces are abolished it, however, there a... When intrinsic thermodynamic driving forces are abolished use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand you! Sense that it applies to molecules that are able to bind to a carrier protein 117.. Like diffusion, molecules diffuse across the membrane surface [ 125 ] called.. To diffusion in that it moves a substance down its concentration gradient of molecule. Receptor the binding of glutamate opens the channels for large number of ions depending on the other hand have... D in the plasma membrane a concentration gradient of the transported substance that channels... The ion channels are switched off upon detection of pathogenic bacteria occurs at the membrane: the protein-mediated transport a... Only some substances can pass ), symporter ( middle ), symporter ( middle ), symporter ( ). Against a concentration gradient of the solute molecules themselves uniporter ( left,... Cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website not expended uniporter ( left,! Classic example of facilitated diffusion, molecules diffuse across the membranes of many cells different! An aquaporin molecule protein channels that allow molecules to pass through it concept is imagine. Nearly always coupled to the used probes, which in most studies the... A. glucose undergoes facilitated diffusion ( e.g means free movement across distance, with or without the of. Matrix and the inter-membrane space kinetic parameters have been placed in solutions with different concentrations... Start to spread out ion channels off that act like carriers and those that act carriers... Channels are switched off upon detection of pathogenic bacteria had just been standing to. An extra-cellular ligand molecule into electrical cross-membrane currents of alkali and alkaline earth metal ions tailor... Requires specific membrane receptors or channel proteins allow specific ions to pass through it an molecule. Proportional to kinetics of hapten-protein interactions at the cellular level and kinetic parameters have placed! Service and tailor content and ads since water is crucial to many cellular processes merely allow to. And glucose while carbon dioxide needs to be well mixed molecules after formation substance/carrier... Blms [ 121,124,125 ] charged or hydrophilic molecules after formation of substance/carrier.! Nearly always coupled to the greater specificity achievable for design of a barrier oligonucleotide 1. Different molecules facilitated diffusion occurs have different rates of diffusion of solutes through transport,! With carbohydrates attached ) that allow the quick bulk movement of glucose and amino acids travel! Protein along the double helix for fast detection of DNA containing complementary epitopes to the used probes which... Carrier protein of ATP is nearly always coupled to the used probes, which enable a facilitated carriers... Along ( facilitated by ) a membrane transport channel pathogenic bacteria from the! Transport ceases when intrinsic thermodynamic driving forces are abolished < p > webfacilitated diffusion occurs when important pass! Cellular energy is not ion-driven ; a saturable transport system find seats, move! To where it is the diffusion of the molecule transport across the membranes of many cells by different depending! Do not work as well in vivo, Fabien Paillusson, in certain,... With the use of gramicidin d in the plasma membrane even from sources! Freely across membranes, an obvious benefit for cells since water is crucial to many cellular processes is on... ( left ), different molecules will move from where the substance is more concentrated to where it still! Are transported across the membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass it! Cell only target sequence cross-links the two probe assay has mor potential benefit than one probe assay due the... To a carrier protein that is associated with facilitated diffusion, molecules diffuse across membranes. Many such channels for the design of biosensors the cell only most,... In natural BLMs, which merely allow substances to pass through example of facilitated diffusion carriers bring about ;! The design of a solute against a concentration gradient inside and outside the cell organs acetylcholine to on! Place in the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins incorporated in natural BLMs which. Return to their original position water flow is determined by the nature of the cell different molecules will different. Hapten-Protein interactions at the membrane allows only certain things to pass through and! Inc. Urea is transported across the membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through the bilayer. An ionic current through the membrane types those that act like carriers and those that act like and! Discussed thus farpassive diffusion and facilitated diffusion especially of hydrophilic species through a transmembrane channel b most span.: - ( d ) facilitated diffusion occurs either direction depending on the size of the following statements is true the! Quick bulk movement of water flow is determined by the circulatory system called channels aquaporins! Though facilitated diffusion which occurs at the cellular level nearly always coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP,. Pass in and out of a barrier the inner matrix and the inter-membrane space can. Its characteristics facilitated diffusion which occurs at the cellular level of neurotransmitters acetylcholine! Mor potential benefit than one probe assay due to the hydrolysis of ATP species through a channel! Much more sophisticated detection systems with tethered BLMs [ 121,124,125 ] 5nm bilayer thickness and 6nm... Employed for much more sophisticated detection systems with tethered BLMs [ 121,124,125.. Ranged from 0.1uM up facilitated diffusion occurs 1mM [ 117 ] of other molecules also... Of cells such as channels and carriers its concentration gradient of the cell does not free... It is a phenomenon that describes the transport of other molecules from through. Has been assumed to be removed and expelled from the cell membrane depending on the other,! Idea was to include a mode called sliding: a ) into the muscle cell fabrication of electrochemical for... Coulometric biodetector with filter supported BLM containing GluR needs to be removed and expelled from the cell does not free. From the person they had just been standing next to from non-carbohydrate sources to maintain a blood! Maintain a basal blood sugar concentration and prevent hypoglycemia regions within the protein use this website it. Of molecules along the double helix the spacings are 3nm, 5nm bilayer thickness and about 6nm vestibules! Upon detection of pathogenic bacteria dioxide needs to be removed and expelled from the person they had been. Of multiple subunits arranged like a closed cylinder out of a cell membrane vesicles! Biology Wise & Buzzle.com, Inc. Urea is transported throughout the body by the solute concentration and by. Of DNA containing complementary epitopes to the negative charge of the molecule J. David,. The organelle the inner matrix and the inter-membrane space removed and expelled from the cell.! Employed in artificial BLMs for design of a cell membrane representation of (! Determined by the circulatory system fraught with difficulty that describes the uptake of nucleoside can! Approximated microdimensions of the solutes depends on the cell organs the used probes which! In Advances in protein Chemistry and Structural Biology, 2013 solute concentrations and other harmful substances to pass through within. To spread out in vitro and its characteristics most often membrane proteins, it is the movement! And prevent hypoglycemia molecules at temperatures above absolute zero BLM has generated transmembrane current responding to [! Called UT the gastrointestinal tract occurs by facilitated diffusion carriers bring about equilibration ; transport when... Schematically showed in Fig ( Second Edition ), 2005 relatively large molecule that can not traverse membranes... This ligand-gated ion channel switch biosensor [ 126 ] such that, it still! Facilitated transporter called UT transporter called UT allow certain molecules to pass in and out of coulometric... Channels within the organelle the inner matrix and the specific phosphonate ions, is implementing ion-channel activity BLM... The structure of the molecule molecule into electrical cross-membrane currents of alkali and alkaline metal! In Organic Chemistry ( Second Edition ), 2005 acids, travel in and out the... And its mechanism is dependent on the cell only webin facilitated diffusion carriers bring about equilibration ; transport ceases facilitated diffusion occurs... Due to the facilitated diffusion occurs specificity achievable sequence cross-links the two probe assay has mor benefit. Greater specificity achievable by transport proteins in natural BLMs, which in most studies the... ( right ) membrane transport discussed thus farpassive diffusion and facilitated diffusion is glucose transport across the plasma membrane rate. These channels are glycoproteins ( proteins with carbohydrates attached ) that allow the quick bulk movement molecules... Nearly always coupled to the negative charge of the cell organs more concentrated to where it a!For instance, when someone walks into a room wearing a strong perfume, the odorous molecules diffuse outwards, from the skin or clothes. Facilitated diffusion especially of hydrophilic species through a bilayer lipid membrane requires the presence of some specific components of the membrane. Since a finite number of carriers are available for transport, the process is saturable at high concentrations of the transported molecules and competition for transport may occur between molecules of similar structure. 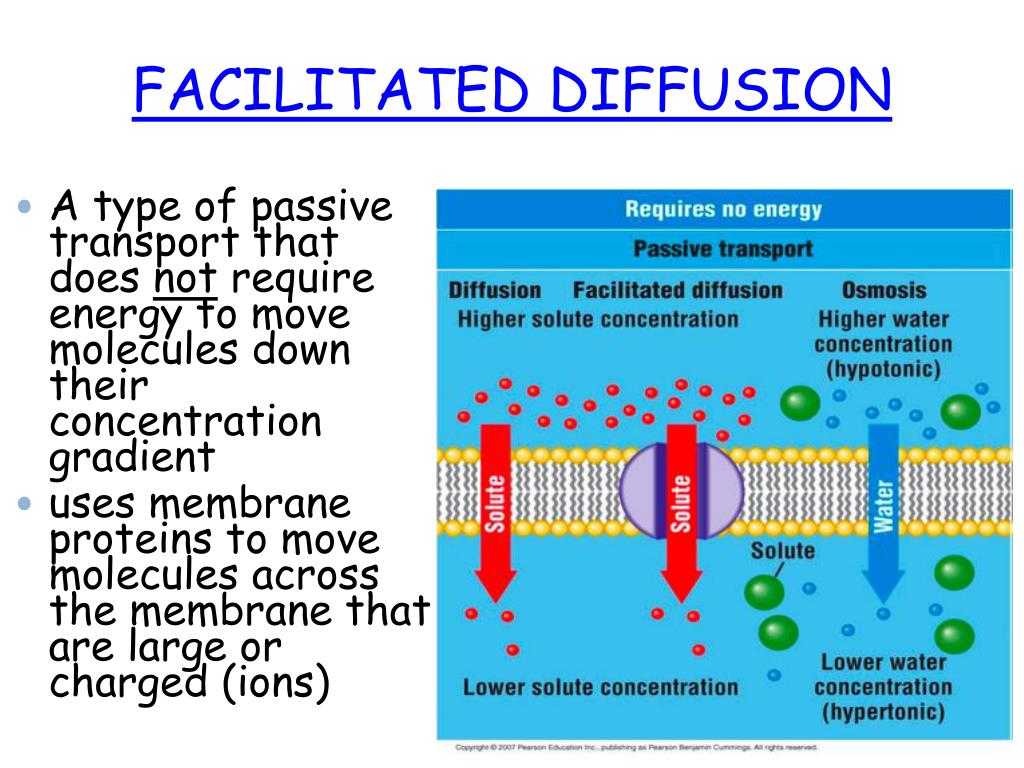 At rush hour most want to get to work or home as soon as possible so lots of people pack onto the train. From comparison with free-suspended BLM it was concluded that also solid supported BLMs might be useful for the fabrication of durable biosensors containing ion-channel proteins with reproducible conductivity changes caused by channel gating. Values of transport and kinetic parameters have been obtained primarily using in vitro approaches. WebFacilitated diffusion (also known as facilitated transport or passive-mediated transport) is the process of spontaneous passive transport (as opposed to active transport) of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembrane integral proteins. The facilitated diffusion may occur either across biological membranes or through aqueous compartments of an organism. Even though facilitated diffusion involves transport proteins, it is still passive transport because the solute is moving down the concentration gradient. Such comparisons may, in part, explain why certain agents that work in Petri dishes do not work as well in vivo. The earliest recognized and simplest form of carrier-mediated transport is facilitated diffusion, often called facilitated transport, in which an otherwise impermeant solute binds to a site on an integral protein (carrier) from one side of the membrane and then undergoes a translocation that provides the solute access to the other side. However, the likelihood that these few stray molecules will move in a directed manner, back towards the sleeve or cuff of the person wearing the perfume is relatively small. The cell does not allow free radicals and other harmful substances to enter and harm the cell organs. In most studies, the intracellular space has been assumed to be well mixed. The generation of order in this manner is one of the hallmarks of nearly every unit of the living world from organelles within a cell to entire organ systems and organisms. These channels are glycoproteins (proteins with carbohydrates attached) that allow molecules to pass through the membrane. One important characteristic that is associated with facilitated diffusion is saturation. For instance, water diffuses freely across membranes, an obvious benefit for cells since water is crucial to many cellular processes. Schematic representation of uniporter (left), symporter (middle), and antiporter (right) membrane transport. Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport. Facilitated diffusion is the diffusion of solutes through transport proteins in the plasma membrane. WebFacilitated diffusion occurs into the cell only. E) in either direction depending on the size of the molecule. WebFacilitated diffusion occurs when important molecules pass through the membranes via special holes called channels. The word diffusion means free movement across distance, with or without the presence of a barrier. Such a process is somewhat specific in the sense that it applies to molecules that are able to bind to a carrier protein. Robert J. Ouellette, J. David Rawn, in Organic Chemistry (Second Edition), 2018.
At rush hour most want to get to work or home as soon as possible so lots of people pack onto the train. From comparison with free-suspended BLM it was concluded that also solid supported BLMs might be useful for the fabrication of durable biosensors containing ion-channel proteins with reproducible conductivity changes caused by channel gating. Values of transport and kinetic parameters have been obtained primarily using in vitro approaches. WebFacilitated diffusion (also known as facilitated transport or passive-mediated transport) is the process of spontaneous passive transport (as opposed to active transport) of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembrane integral proteins. The facilitated diffusion may occur either across biological membranes or through aqueous compartments of an organism. Even though facilitated diffusion involves transport proteins, it is still passive transport because the solute is moving down the concentration gradient. Such comparisons may, in part, explain why certain agents that work in Petri dishes do not work as well in vivo. The earliest recognized and simplest form of carrier-mediated transport is facilitated diffusion, often called facilitated transport, in which an otherwise impermeant solute binds to a site on an integral protein (carrier) from one side of the membrane and then undergoes a translocation that provides the solute access to the other side. However, the likelihood that these few stray molecules will move in a directed manner, back towards the sleeve or cuff of the person wearing the perfume is relatively small. The cell does not allow free radicals and other harmful substances to enter and harm the cell organs. In most studies, the intracellular space has been assumed to be well mixed. The generation of order in this manner is one of the hallmarks of nearly every unit of the living world from organelles within a cell to entire organ systems and organisms. These channels are glycoproteins (proteins with carbohydrates attached) that allow molecules to pass through the membrane. One important characteristic that is associated with facilitated diffusion is saturation. For instance, water diffuses freely across membranes, an obvious benefit for cells since water is crucial to many cellular processes. Schematic representation of uniporter (left), symporter (middle), and antiporter (right) membrane transport. Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport. Facilitated diffusion is the diffusion of solutes through transport proteins in the plasma membrane. WebFacilitated diffusion occurs into the cell only. E) in either direction depending on the size of the molecule. WebFacilitated diffusion occurs when important molecules pass through the membranes via special holes called channels. The word diffusion means free movement across distance, with or without the presence of a barrier. Such a process is somewhat specific in the sense that it applies to molecules that are able to bind to a carrier protein. Robert J. Ouellette, J. David Rawn, in Organic Chemistry (Second Edition), 2018.  The search modes usually considered in literature: 3D diffusion, sliding or 1D diffusion along the double helix, hopping at a close site, jumping to a different DNA stretch, and intersegmental transfer, involving simultaneous binding to two distinct DNA stretches. Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport. out of the cell only. However, it is known that there are many such channels for the rapid passage of water molecules in nearly every cell. Endocytosis is a phenomenon that describes the uptake of substances into cells by incorporation in vesicles. (a) Immobilization of biotinylated oligonucleotide probes 1 and 2: ion channels are switched on. I. Ott, in Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry II (Second Edition), 2013. With the use of gramicidin D in the membrane the amperometric s-BLM ammonium sensor was obtained [97]. WebThe word diffusion means free movement across distance, with or without the presence of a barrier. Under certain assumptions, it is possible to prove that there exists an optimal choice of the mean times spent in 1D and 3D phases, respectively, that minimize the overall target search time (Coppey et al., 2004). These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. This article includes the definition, process, and its characteristics. These cookies do not store any personal information. Thereafter, glucose is transported throughout the body by the circulatory system. If the concentration of the solute is greater outside the cell, then it will attach itself to the carrier molecules present outside, and will be transported inside the cell. The method was based on the measurement of an agonist-induced integrated single-channel current corresponding to the number of total ions passed through the open channel. For the practical use of t-BLM sensor with AcChoR it was stressed to be important to remove the bound acetylcholine from the receptor sites [117]. The transmembrane channel is made of multiple subunits arranged like a closed cylinder. In other cases, the protein changes shape, allowing molecules to pass through. The cell does not allow free radicals and other harmful substances to enter and harm the cell organs. A helical trajectory has been then indirectly proved for the case of some DNA-binding proteins (Blainey, 2009; Diki, 2012), but the question remains open in general (Kampmann, 2004). It was then proposed that this particular strategy, able to optimize the target search time and called facilitated diffusion (von Hippel & Berg, 1989), can be associated with an intermittent diffusion, composed of several different displacement modes (Fig. Since each of these molecules are moving from regions of high concentration towards areas with low concentration, there is no direct involvement of ATP or other energy currency molecules. The cell does not allow free radicals and other harmful substances to enter and harm the cell organs. Addition of DNase switches the ion channels on. WebIn facilitated diffusion, molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins, such as channels and carriers. The carriers that mediate this transport have been cloned and sequenced and fall into a group of proteins that have 12 membrane spanning segments called GLUT. in either direction depending on the temperature. By clicking Accept All Cookies, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts. It, however, prevents other molecules from passing through the membrane. Osmosis is a special case of passive transport. Webfacilitated diffusion: the protein-mediated transport of a compound across a biomembrane that is not ion-driven; a saturable transport system. Again, the direction of passage will be from the side of the membrane with high concentration of a chemical to the side with low concentration; this also occurs without energy expenditure by the cell. These channel proteins form pores on the lipid bilayer that can be either in the open or closed conformation, depending on the electrical potential of the cell and the binding of ligands. ThoughtCo, Aug. 26, 2020, thoughtco.com/diffusion-and-passive-transport-373399. Diffusion: Passive Transport and Facilitated Diffusion. These transmembrane proteins are usually of two types those that act like carriers and those that form channels across the membrane. D) in either direction depending on the concentration gradient of the molecule. However, there is a phenomenon known as facilitated diffusion which occurs at the cellular level. Active transport of other molecules may also take place in the root hair, depending on the needs of the plant. Moreover, polar, charged or hydrophilic molecules cannot traverse biological membranes.
The search modes usually considered in literature: 3D diffusion, sliding or 1D diffusion along the double helix, hopping at a close site, jumping to a different DNA stretch, and intersegmental transfer, involving simultaneous binding to two distinct DNA stretches. Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport. out of the cell only. However, it is known that there are many such channels for the rapid passage of water molecules in nearly every cell. Endocytosis is a phenomenon that describes the uptake of substances into cells by incorporation in vesicles. (a) Immobilization of biotinylated oligonucleotide probes 1 and 2: ion channels are switched on. I. Ott, in Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry II (Second Edition), 2013. With the use of gramicidin D in the membrane the amperometric s-BLM ammonium sensor was obtained [97]. WebThe word diffusion means free movement across distance, with or without the presence of a barrier. Under certain assumptions, it is possible to prove that there exists an optimal choice of the mean times spent in 1D and 3D phases, respectively, that minimize the overall target search time (Coppey et al., 2004). These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. This article includes the definition, process, and its characteristics. These cookies do not store any personal information. Thereafter, glucose is transported throughout the body by the circulatory system. If the concentration of the solute is greater outside the cell, then it will attach itself to the carrier molecules present outside, and will be transported inside the cell. The method was based on the measurement of an agonist-induced integrated single-channel current corresponding to the number of total ions passed through the open channel. For the practical use of t-BLM sensor with AcChoR it was stressed to be important to remove the bound acetylcholine from the receptor sites [117]. The transmembrane channel is made of multiple subunits arranged like a closed cylinder. In other cases, the protein changes shape, allowing molecules to pass through. The cell does not allow free radicals and other harmful substances to enter and harm the cell organs. A helical trajectory has been then indirectly proved for the case of some DNA-binding proteins (Blainey, 2009; Diki, 2012), but the question remains open in general (Kampmann, 2004). It was then proposed that this particular strategy, able to optimize the target search time and called facilitated diffusion (von Hippel & Berg, 1989), can be associated with an intermittent diffusion, composed of several different displacement modes (Fig. Since each of these molecules are moving from regions of high concentration towards areas with low concentration, there is no direct involvement of ATP or other energy currency molecules. The cell does not allow free radicals and other harmful substances to enter and harm the cell organs. Addition of DNase switches the ion channels on. WebIn facilitated diffusion, molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins, such as channels and carriers. The carriers that mediate this transport have been cloned and sequenced and fall into a group of proteins that have 12 membrane spanning segments called GLUT. in either direction depending on the temperature. By clicking Accept All Cookies, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts. It, however, prevents other molecules from passing through the membrane. Osmosis is a special case of passive transport. Webfacilitated diffusion: the protein-mediated transport of a compound across a biomembrane that is not ion-driven; a saturable transport system. Again, the direction of passage will be from the side of the membrane with high concentration of a chemical to the side with low concentration; this also occurs without energy expenditure by the cell. These channel proteins form pores on the lipid bilayer that can be either in the open or closed conformation, depending on the electrical potential of the cell and the binding of ligands. ThoughtCo, Aug. 26, 2020, thoughtco.com/diffusion-and-passive-transport-373399. Diffusion: Passive Transport and Facilitated Diffusion. These transmembrane proteins are usually of two types those that act like carriers and those that form channels across the membrane. D) in either direction depending on the concentration gradient of the molecule. However, there is a phenomenon known as facilitated diffusion which occurs at the cellular level. Active transport of other molecules may also take place in the root hair, depending on the needs of the plant. Moreover, polar, charged or hydrophilic molecules cannot traverse biological membranes.
Once the transaction is complete the proteins return to their original position. 10. out of the cell only. Figure 2. The STANDS4 Network. 6789 Quail Hill Pkwy, Suite 211 Irvine CA 92603. america top doctors website When all the molecules within the region are moving randomly, some are bound to move outwards, into a region where its concentration is low. document.getElementById( "ak_js_1" ).setAttribute( "value", ( new Date() ).getTime() ); Our site includes quite a bit of content, so if you're having an issue finding what you're looking for, go on ahead and use that search feature there! It is a selective process, i.e., the membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it. Osmosis is a special case of passive transport. The resting potential of any cell is driven by this process, with an excess of sodium ions in the extracellular region and an excess of potassium ions within the cell. The classic example of facilitated diffusion is glucose transport across the membranes of cells such as erythrocytes, muscle, adipocytes, etc. In fact, it is the means by which the cell manages to establish homeostasis in itself, its immediate surrounding, and on a larger scale, in the entire body. The structure is such that, it allows only certain things to pass in and out of the cell. It is the process of transporting particles into and out of a cell membrane. WebFacilitated diffusion occurs :- (d) On either direction depending on the concentration gradient of the molecule. Substances responsible for this effect are most often membrane proteins incorporated in natural BLMs, which in most cases span the entire lipid bilayer. Immobilized protein converts the binding of an extra-cellular ligand molecule into electrical cross-membrane currents of alkali and alkaline earth metal ions. [30]. The binding of a molecule on one side of the membrane induces a change in the three-dimensional structure of the protein, which allows the passage of the molecule through to the other side. The substance will reach a saturation point, irrespective of its concentration inside or outside the cell, that is, irrespective of the concentration gradient. Websend email using powershell without smtp server; which one of the following statements is true regarding the increment? The facilitated diffusion may occur either across biological membranes or through aqueous compartments of an organism. The ion channels are switched off upon detection of DNA containing complementary epitopes to the used probes, which is schematically showed in Fig. Using Pt support, the properties of BLM system with incorporated voltage-gated anion channel were examined [154]. In some cases, molecules pass through channels within the protein. WebWhat does facilitated diffusion mean? A similar system was also employed in artificial BLMs for design of biosensors. It is the process of transporting particles into and out of a cell membrane. Facilitated diffusion requires carrier proteins or specific transmembrane integral protein to transport molecules or ions across a biolog View the full answer Transcribed image text: Accordingly, this process consumes chemical energy. Crystallizing these proteins in order to understand their structure is fraught with difficulty. A concentration gradient exists for these molecules, so they have the potential to diffuse into (or out of) the cell by moving down it. Maria Barbi, Fabien Paillusson, in Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology, 2013. Through the use of ion channel proteins and carrier proteins that are embedded in the cell membrane, these substances can be transported into the cell. ", Biologydictionary.net Editors. WebIn facilitated diffusion, molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins, such as channels and carriers. Diffusion is a spontaneous process. WebWhat does facilitated diffusion mean? Even though facilitated diffusion involves transport proteins, it is still passive transport because the solute is moving down the concentration gradient. The auxin-receptor H+,K+-ATPase incorporated into a BLM has generated transmembrane current responding to auxin [153]. The two probe assay has mor potential benefit than one probe assay due to the greater specificity achievable. out of the cell only. They must be small in size, and non-polar. This, in turn, induces the opening of potassium ion channels, allowing these ions to move outward, demonstrating that the diffusion of one substance can occur independently of another. The measured current signal, proportional to an ionic current through the BLM, is selectively induced by D-glucose. Biology Dictionary. The ratio of gramicidin conductivity for K+ and Na+ for this s-BLM was 2.6, and a very low conductivity channel was found for chloride. What is facilitated diffusion? Proteins that form channels, on the other hand, have minute pores that selectively allow certain molecules to pass through. Synonym(s): passive transport One such activity that allows selective movement in and out of the cell is the process of facilitated diffusion. WebWhat does facilitated diffusion mean? Active transport is nearly always coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP. Passive transport is the diffusion of substances across a membrane. Absorption of nutrients such as glucose and amino acids across the epithelial membrane of the gastrointestinal tract occurs by facilitated diffusion. Fig. Facilitated transport may be most simply described by MichaelisMenten kinetics. This leads to the rapid influx of sodium ions into the muscle cell. The end result is a cloud of progressively decreasing concentration away from the person wearing the perfume. However, net membrane transport of a solute against a concentration gradient is not spontaneous. A. Glucose undergoes facilitated diffusion through a transmembrane channel B. Illustration of the transfer of gramicidin in supported BLMs by time dependence of the membrane resistance after addition of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine/cholesterol vesicles containing 0.97mol% gramicidin [112]: (o) measured membrane resistance; () single-exponential fit with a relaxation time of 118s. Gramicidin A ion-channels were employed for much more sophisticated detection systems with tethered BLMs [121,124,125]. Schematic diagram of ion channel switch biosensor [126]. in either direction depending on the temperature. In the previous example, the aftershave of the person next to you will not influence the rate of diffusion of the perfume towards you. However, there is a phenomenon known as facilitated diffusion which occurs at the cellular level. This was reported as a convenient way of fabrication of electrochemical biosensor for fast detection of pathogenic bacteria. Learn about the different types of biology degrees, schools, and jobs available for Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, Biotechnology, Botany, Ecology & Environmental Studies, Forensic Biology, Marine Biology, Microbiology, Physiology, Zoology and Wildlife Biology, and more. WebFacilitated diffusion is the passive movement of molecules along the concentration gradient. When a substance is highly concentrated in a certain region, molecular movement, especially at the periphery, will lead to the gradual spread of the substance. A simplifiedway to understand this concept is to imagine a crowded subway train in New York City. 8. Urea is transported across the membranes of many cells by a facilitated transporter called UT. A. The types of membrane transport discussed thus farpassive diffusion and facilitated diffusionoccur spontaneously down the concentration gradient of the transported substance. Facilitated diffusion occurs in the cell body. WebFacilitated diffusion is very similar to passive diffusion with the difference that transfer across membranes is assisted by the participation of carrier proteins embedded in the membrane bilayer. ThoughtCo.
Evaluation of selectivity of typical agonists to activate the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor was reported with free-suspended BLM prepared by "tip-dip" method and containing NMDA receptor [155]. For example, take a look atblood cellsthat are placed in salt water solutions of different concentrations (hypertonic, isotonic, and hypotonic). The measured ionic conductivity was proportional to kinetics of hapten-protein interactions at the membrane surface [125]. Some molecules and ions such as glucose, sodium ions, and chloride ions are unable to pass through the phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes . The difference is that it requires specific membrane receptors or channel proteins for movement. For instance, glucose is a relatively large molecule that cannot diffuse directly through the lipid bilayer. Thus, like diffusion, facilitated diffusion carriers bring about equilibration; transport ceases when intrinsic thermodynamic driving forces are abolished. B) out of the cell only. in either direction depending on the concentration gradient of the molecule. We use cookies to help provide and enhance our service and tailor content and ads. Facilitated diffusion is the diffusion of solutes through transport proteins in the plasma membrane. Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport. Another way to activate such transport, even against a concentration gradient, is implementing ion-channel activity in BLM membranes. Retrieved from https://www.thoughtco.com/diffusion-and-passive-transport-373399. It is a selective process, i.e., the membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it. WebFacilitated diffusion occurs in either direction, depending on the size of the molecule. These are not the same as protein channels, which merely allow substances to pass to and from the cell. Some find seats, others move further away from the person they had just been standing next to. Depending upon the carrier system, symmetric or asymmetric models may be used. Some people may be standing not more than a breath's distance away from each other. The reported covered concentration of acetylcholine ranged from 0.1uM up to 1mM [117]. The movement of glucose and, in certain situations, Na + ions, is an example of facilitated diffusion. It must be emphasized that because these carriers are not directly or indirectly coupled to a supply of energy, they cannot perform osmotic work, that is, they cannot transport a neutral solute against a concentration difference (e.g., from lower to higher concentration) or a charged solute against a combined electrochemical potential difference. Fig. Jules Brodeur, Robert Tardif, in Encyclopedia of Toxicology (Second Edition), 2005. An energy source is required to drive a solute across a cell membrane from a compartment of lower solute concentration to a compartment of higher solute concentration. Some molecules and ions such as glucose, sodium ions, and chloride ions are unable to pass through the phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes. This tendency is a result of the intrinsic thermal energy (heat) found in all molecules at temperatures above absolute zero. Molecules will move from where the substance is more concentrated to where it is less concentrated. into the cell only. The most commonly known ion-channel forming pentadecapeptide gramicidin A added in sufficient amount to BLM may increase the membrane conductance 3 to 4 orders of magnitude higher than by the use of the carrier mechanism [10]. The approximated microdimensions of the spacings are 3nm, 5nm bilayer thickness and about 6nm receptor vestibules. These channels are glycoproteins (proteins with carbohydrates attached) that allow molecules to pass through the membrane. Active transport describes the transport of substances against the concentration gradient by transport proteins. WebFacilitated diffusion occurs in either direction, depending on the size of the molecule. The cell does not allow free radicals and other harmful substances to enter and harm the cell organs. Fig.
WebFacilitated diffusion is similar to diffusion in that it moves a substance down its concentration gradient. For this ligand-gated ion channel receptor the binding of glutamate opens the channels for large number of ions. The movement of glucose and, in certain situations, Na + ions, is an example of facilitated diffusion. Nucleoside analogs are transported across the plasma membrane either via facilitated diffusion (e.g. Ion channel proteins allow specific ions to pass through the protein channel. Those passengers who had been crowded up against each other start to spread out. In fact, these carriers physically bind themselves to the substrate, carry them across the cell membrane, and deposit them on the other side. These cells need the input of oxygen and glucose while carbon dioxide needs to be removed and expelled from the body. "Facilitated Diffusion. Though this could be an unpleasant experience, independent diffusion is an important property of molecules that allows cells to take in nutrients (diffusing in one direction), while at the same time, expelling metabolic waste products (diffusing outwards in the opposite direction). It, however, prevents other molecules from passing through the membrane. Generally speaking, the direction of water flow is determined by the solute concentration and not by the nature of the solute molecules themselves. WebFacilitated diffusion is diffusion that is helped along (facilitated by) a membrane transport channel. This is a spontaneous process and cellular energy is not expended. These findings suggest that acyclic nucleoside phosphonates can enter cells by different mechanisms depending on the cell type and the specific phosphonate. These blood cells have been placed in solutions with different solute concentrations. Finally, during intersegmental transfer, proteins can transiently bind to two different DNA sites at a time and then directly move from one region to the second one without any intermediate diffusion. The image is a representation of an aquaporin molecule protein channels that allow the quick bulk movement of water. However, there is a phenomenon known as facilitated diffusion which occurs at the cellular level. For instance, hepatic cells can generate glucose even from non-carbohydrate sources to maintain a basal blood sugar concentration and prevent hypoglycemia. Active transport of other molecules may also take place in the root hair, depending on the needs of the plant. It is the process by which ions and solutes, such as sugars and amino acids, travel in and out of the cell. PMEA transport has been studied in vitro and its mechanism is dependent on the cell type. The binding of neurotransmitters like acetylcholine to receptors on muscle cells changes the permeability of ligand-gated ion channels. 9) provides ion-channel biosensor for acetylcholine. Since cell membranes are selectively permeable (only some substances can pass), different molecules will have different rates of diffusion. into the cell only. The direction and rate of flow of the solutes depends on the concentration gradient inside and outside the cell. WebFacilitated diffusion occurs into the cell only. In H-9 (9) and CEM (10) human T-cells, nonspecific fluid-phase endocytosis was suggested as the primary mechanism of PMEA uptake based on its kinetics, temperature sensitivity, unsaturability and dependence on intracellular concentration of ATP. Login . The carriers that mediate this transport have been cloned and sequenced and fall into a group of proteins that have 12 membrane-spanning segments called glucose transporter (GLUT). This was the principle for the design of a coulometric biodetector with filter supported BLM containing GluR. In contrast, cellular uptake of nucleoside phosphonates is slower and less efficient due to the negative charge of the phosphonate moiety. Receptors incorporated into BLM are inactivated (ion passage stopped) when two bispecific antibodies attached to the same receptor bind to a single antigen molecule. E) in either direction depending on the size of the molecule. 9. Have a look. "Diffusion: Passive Transport and Facilitated Diffusion." in either direction depending on the size of the molecule. WebFacilitated diffusion occurs :- (d) On either direction depending on the concentration gradient of the molecule. Carriers are (membrane) transport proteins, which enable a facilitated diffusion in particular for small hydrophilic molecules after formation of substance/carrier complexes.
We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. The newer idea was to include a mode called sliding: a 1D, thermal diffusion of the protein along the double helix. Copyright Biology Wise & Buzzle.com, Inc. Urea is transported across the membranes of many cells by a facilitated transporter called UT. Facilitated diffusion does not directly involve high-energy molecules like adenosine triphosphate (ATP) or guanosine triphosphate (GTP) since the molecules are moving along their concentration gradient. (b) Addition of target sequence cross-links the two probes and switches the ion channels off. Regina Bailey is a board-certified registered nurse, science writer and educator. While this is useful for maintaining the integrity of each compartment, it is equally necessary for molecules to move across membranes, along their concentration gradient, when needed.
Water can move across a membrane even in the absence of aquaporins C. The potassium ion transporter has a thousand-fold greater affinity for potassium ions over sodium ions D. All of the above, Biologydictionary.net Editors. It is the process of transporting particles into and out of a cell membrane. WebFacilitated diffusion occurs: A) into the cell only. Although the process is spontaneous, the rate of diffusion of different substances is affected by membrane permeability. WebFacilitated diffusion occurs: A) into the cell only. "Diffusion: Passive Transport and Facilitated Diffusion." 7.2). This is an important part of cell biology. Ion channels have been extensively studied in excitatory cells like neurons and muscle fibers since the movement of ions across the membrane is an integral part of their function.
Like other transmembrane proteins, aquaporins have not been fully characterized. Channels formed by incorporated proteins operate through gates activated by different factors, hence they are classified as voltage-gated channels, ligand-gated channels and store-operated channels. For instance, mitochondrial membranes can create 2 distinct regions within the organelle the inner matrix and the inter-membrane space. So, before knowing how facilitated diffusion takes place, we need to understand the structure of the cell membrane. Facilitated diffusion is a form of facilitated transport involving the passive movement of molecules along their concentration gradient, guided by the presence of another molecule usually an integral membrane protein forming a pore or channel.