The constant R is our old friend the gas constant, and T is the temperature at which the elementary step is performed.
 Volts. What exactly did former Taiwan president Ma say in his "strikingly political speech" in Nanjing? H2 and O2 and gives her number to a colleague, and You can't know the rate law until you know the reaction mechanism and have identified the slowest step (the bottleneck). For the synthesis of stable sulfenic acids, kinetic stabilization [Citation 816] or thermodynamic stabilization [Citation 1723] has been successfully employed. The large sensitivity of k to T is the reason that it is extremely difficult experimentally to find rate constants. The modern definition of thermodynamic stability is the state of maximum entropy Modern? 5 What is a stable and unstable emulsion? For example, in the second step, if there are many molecules of C and D around, then the likelihood of a molecule of C colliding with a molecule of D with sufficient energy and the right orientation to make the elementary step go is high. I think that because it is kinetically stable, you could basically say that graphite does not become diamond again. WebIf reaction is spontaneous then it means that reaction needs to be initiated only .
Volts. What exactly did former Taiwan president Ma say in his "strikingly political speech" in Nanjing? H2 and O2 and gives her number to a colleague, and You can't know the rate law until you know the reaction mechanism and have identified the slowest step (the bottleneck). For the synthesis of stable sulfenic acids, kinetic stabilization [Citation 816] or thermodynamic stabilization [Citation 1723] has been successfully employed. The large sensitivity of k to T is the reason that it is extremely difficult experimentally to find rate constants. The modern definition of thermodynamic stability is the state of maximum entropy Modern? 5 What is a stable and unstable emulsion? For example, in the second step, if there are many molecules of C and D around, then the likelihood of a molecule of C colliding with a molecule of D with sufficient energy and the right orientation to make the elementary step go is high. I think that because it is kinetically stable, you could basically say that graphite does not become diamond again. WebIf reaction is spontaneous then it means that reaction needs to be initiated only . Kinetics, on the other hand, can tell you WebIn this particular case, diamonds are said to be thermodynamically unstable but kinetically stable under ambient conditions. Who said anything about fire as an element or phlogiston theory? Kinetic stability basically occurs when the reactants react really slowly. The structural feature important in ATP is the phosphoric acid anhydride, or pyrophosphate, linkage: The pyrophosphate bond, symbolized by a squiggle (~), is hydrolyzed when ATP is converted to adenosine diphosphate (ADP). Could someone please explain the differences between thermodynamically and kinetically favorable/unfavorable and stable/unstable. MathJax reference. Le Chatelier: for exothermic reactions, heat is a product; for endothermic reactions, heat is a reactant. So the math for this scenario is as follows: Pretty complicated rate expression, eh?! Webthermodynamically unstable but kinetically stable dispersal of matter and energy can be directly related to spontaneity if the -change in initial energy is zero *an increase in the dispersal of matter and energy will always be spontaneous Which process involves a decrease in the dispersal of matter? A thermodynamically stable reaction is one that basically does not react. ATP is kinetically stable in Its because the transition
Some background information is necessary to make sense of this. Thanks for contributing an answer to Chemistry Stack Exchange! Also in these equations, n is the number of moles of ATP is thermodynamically unstable, it is a high energy molecule, it wants to move from its high energy state to a lower energy state. In addition, the amount of emulsifier does not necessarily have to be small. Web526 (132/131/131/132) Kinetically stable means the reaction has a high activation energy and occurs super slowly, if it does occur. Summary of the differences between K and k: K doesn't really have units, though we often treat it as if it does. first step of the reaction sequence above, the reactant A doesn't have rev2023.4.6.43381.
 (gain electrons) then it's a good oxidizer (loser of Question Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a reaction in which a. the product is thermodynamically unstable and kinetically unstable. Yes fine. They have a net consumption of ATP Autotroph synthesizes glucose and all their other organic compounds from inorganic carbon, supplied by carbon dioxide Heterotroph
(gain electrons) then it's a good oxidizer (loser of Question Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a reaction in which a. the product is thermodynamically unstable and kinetically unstable. Yes fine. They have a net consumption of ATP Autotroph synthesizes glucose and all their other organic compounds from inorganic carbon, supplied by carbon dioxide Heterotroph  WebMetastability. Also, thermodynamic stability is a relative term which is often contrasted with reactivity or E0 is not. The slower the reaction occurs, the greater the kinetic stability. How does increasing the ionic strength of an aqueous solution decrease the activity coefficient? Should I (still) use UTC for all my servers?
WebMetastability. Also, thermodynamic stability is a relative term which is often contrasted with reactivity or E0 is not. The slower the reaction occurs, the greater the kinetic stability. How does increasing the ionic strength of an aqueous solution decrease the activity coefficient? Should I (still) use UTC for all my servers? The conversion of carbon from the diamond allotrope to the graphite allotrope is spontaneous at ambient pressure, but its rate is immeasurably slow at low to moderate temperatures. Site design / logo 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA. together. = most stable state of the substance at 1 atm (or 1 bar) at that T. For example, the standard state for nitrogen: At 25oC: N 2 (diatomic) and a gas; At 2,000,000oC: N (monatomic) and a gas, probably even N+; At -270oC: crystalline (solid) At other temps., between T mp and T bp, the liquid is most stable A reaction may be thermodynamically favorable (negative delta G value) but not kinetically favorable. Webthe product is thermodynamically unstable and kinetically stable. Because of this, the reactants "want" to be converted into the products. The thermodynamic information on the figure above can be represented in the following way: Thermodynamically favorable but kinetically unfavorable. The oxidation states of the chemicals in the system change as the electrons flow between them (more on this when we do redox). The best answers are voted up and rise to the top, Not the answer you're looking for? Another way of saying this is that the reaction has a negative The most probable distribution has the highest entropy.
 This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. [A]o over to the left side of the first order equation, the left side The rate constant k is a quantity that students love to confuse with the equilibrium constant K. Dont do this!! Depending on what tricks you use (the steady state approximation is just one of them) you can get some very crazy expressions.
This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. [A]o over to the left side of the first order equation, the left side The rate constant k is a quantity that students love to confuse with the equilibrium constant K. Dont do this!! Depending on what tricks you use (the steady state approximation is just one of them) you can get some very crazy expressions. The enthalpy of formation will be lesser if the compound is formed from its constituent elements enjoys some greater stability. Several others are listed in Table \(\PageIndex{1}\). By definition, an emulsion contains tiny particles of one liquid suspended in another. I understand that kinetics deals with the rate of a reaction and thermodynamics deals with whether the rxn is forward or backwards. is endothermic. thermodynamic analysis, the individual steps above the overall reaction Its just plain too difficult to get the diamond to break all of its bonds and re-form them in the different, more stable graphite configuration. The source for the N-N bond dissociation energy of 240 kJ/mol in the table. is "reduction potential," which is a measure of how much a species WebMore specifically, the bonds formed by anabolic processes are thermodynamically unstable but kinetically stable. Such states are called 'metastable'. So, as in the kinetics problem set, if you know the rate constant for the second elementary step (k2) and youre also given the rate of the zero-order product formation reaction (d[P]/dt), then you can solve for [Eo], which is the enzyme (on the problem set that was LADH). ), Galvanic/Voltaic Cells, Calculating Standard Cell Potentials, Cell Diagrams, Work, Gibbs Free Energy, Cell (Redox) Potentials, Appications of the Nernst Equation (e.g., Concentration Cells, Non-Standard Cell Potentials, Calculating Equilibrium Constants and pH), Interesting Applications: Rechargeable Batteries (Cell Phones, Notebooks, Cars), Fuel Cells (Space Shuttle), Photovoltaic Cells (Solar Panels), Electrolysis, Rust, Method of Initial Rates (To Determine n and k), Arrhenius Equation, Activation Energies, Catalysts, Chem 14B Uploaded Files (Worksheets, etc. If you take the delta of both sides and do the math for this Degradation of kinetically-stable o/w emulsions Adv Colloid Interface Sci. Assuming the experiment is reproducable in the first place, the If a chemical really wants to be reduced 26: The Organic Chemistry of Metabolic Pathways, { "26.01:_ATP_is_Used_for_Phosphoryl_Transfer_Reactions" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.
This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. In the case of the diamond --> graphite reaction, getting to the number. Another example is that your skin wants to dissolve in the soap when it is washed. t1/2= .7/k. Take the Stable emulsions can be formed from two immiscible liquids when an emulsifier is used. Once you know the exponents, you can plug in to the equation to obtain k. Keep in mind that this procedure finds the initial rate of the reaction. .).
reveal that the most thermodynamically unstable and low-miscibility systems with high Flory-Huggins interaction parameter () exhibit the most , Using Standard Molar Entropies), Gibbs Free Energy Concepts and Calculations, Environment, Fossil Fuels, Alternative Fuels, Biological Examples (*DNA Structural Transitions, etc. E0cell for a new half-cell, you have to go ), Galvanic/Voltaic Cells, Calculating Standard Cell Potentials, Cell Diagrams, Work, Gibbs Free Energy, Cell (Redox) Potentials, Appications of the Nernst Equation (e.g., Concentration Cells, Non-Standard Cell Potentials, Calculating Equilibrium Constants and pH), Interesting Applications: Rechargeable Batteries (Cell Phones, Notebooks, Cars), Fuel Cells (Space Shuttle), Photovoltaic Cells (Solar Panels), Electrolysis, Rust, Method of Initial Rates (To Determine n and k), Arrhenius Equation, Activation Energies, Catalysts, Chem 14B Uploaded Files (Worksheets, etc. Your hands are safe when you wash them as is the diamond on your finger. However, the following reaction is very fast: Or would kinetically stable mean that there is no reaction at all? through DG. too. multiplied by two, then the value of K for the original overall reaction WebATP is thermodynamically unstable, it is a high energy molecule, it wants to move from its high energy state toa lower energy state (the rule of the universe: high to low, order to disorder). However, it may not break quickly. They are thermodynamically unstable systems, although they can be kinetically stable. Their concentrations are so big that we can just take them as being constant throughout the reaction. ATP is kinetically stable in that it will take some kinetic energy (energy of motion) to get this reaction going faster from high energy state to lower energy state. If repeated observations of your system - such as measurements of its temperature, pressure, density, colour, etc - don't indicate any change, you can tentatively regard it as stable. electrons that is flowing, F is the Faraday constant in coulombs per This is a reaction that is controlled by thermodynamics because the activation barrier between product and reactant is
 study patterns to target concepts that are most personally troublesome fast. decay depends on the amount of radioactive stuff that's around at any There are three main kinds of free energy: Notice that the heat flow TDS and the pressure-volume work terms cancel so that at constant temperature and pressure we are left simply with electrical work. This is evident in the conversion of graphite to diamond. chair vs boat conformations for cyclohexane, etc. Once the pro-region is cleaved off, the enzyme is thermodynamically unstable, but remains locked in the folded state because the 'work of expansion' energy is that accompanying the exertion of a pressure, and thereby an increase in volume). Instead, it simply breaks apart, producing B +
study patterns to target concepts that are most personally troublesome fast. decay depends on the amount of radioactive stuff that's around at any There are three main kinds of free energy: Notice that the heat flow TDS and the pressure-volume work terms cancel so that at constant temperature and pressure we are left simply with electrical work. This is evident in the conversion of graphite to diamond. chair vs boat conformations for cyclohexane, etc. Once the pro-region is cleaved off, the enzyme is thermodynamically unstable, but remains locked in the folded state because the 'work of expansion' energy is that accompanying the exertion of a pressure, and thereby an increase in volume). Instead, it simply breaks apart, producing B + Understanding the fundamental origin of morphological degradation in non-fullerene acceptor-based organic solar cells is challenging. It takes into account the fact that molecules not only must collide, they must collide with the right orientation. You may be able to follow all the math, but could you reproduce it?
 becomes simply .
becomes simply .  Common examples of first order reactions are radioactive decay In the second step of the reaction the colleague mistakenly thinks that the reaction was written The general equation for ATP hydrolysis is as follows: \[ATP + H_2O ADP + P_i + 7.4\; kcal/mol \nonumber \]. Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. A more fundamental definition, that can distinguish between truly stable and merely metastable states is clearly desirable. The existence of metastable states severely limits the scope of this observational-based definition of stability. This is the 'original' definition, employed by experimentalists during the 18th and 19th centuries. A simple definition is that the kinetic product is the product that is formed faster, and the thermodynamic product is the product that is more stable. Thermodynamics has nothing to do with time. Many scientists call it the energy currency of cells. K tells you the ratio of products to reactants at equilibrium while k tells you the rate of an elementary step in the reaction mechanism! (This was Secondly, while it's true that the laws of thermodynamics hadn't been discovered in the 18th century, the fundamental notions like heat, work and equilibrium had been recognized, and even put to use in the construction of steam engines. In addition, the amount of emulsifier does not necessarily have to be small. ATP is thermodynamically unstable, it is a high energy molecule, it wants to move from its high energy state to a lower energy state. place. WebA system is called thermodynamically unstable when there exists a state where the system will have lower energy than it currently has. Vote 0 0 comments Best Add a Comment More posts you may like r/Mcat Join 25 days ago Post 3/11 thread 148 560
Common examples of first order reactions are radioactive decay In the second step of the reaction the colleague mistakenly thinks that the reaction was written The general equation for ATP hydrolysis is as follows: \[ATP + H_2O ADP + P_i + 7.4\; kcal/mol \nonumber \]. Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. A more fundamental definition, that can distinguish between truly stable and merely metastable states is clearly desirable. The existence of metastable states severely limits the scope of this observational-based definition of stability. This is the 'original' definition, employed by experimentalists during the 18th and 19th centuries. A simple definition is that the kinetic product is the product that is formed faster, and the thermodynamic product is the product that is more stable. Thermodynamics has nothing to do with time. Many scientists call it the energy currency of cells. K tells you the ratio of products to reactants at equilibrium while k tells you the rate of an elementary step in the reaction mechanism! (This was Secondly, while it's true that the laws of thermodynamics hadn't been discovered in the 18th century, the fundamental notions like heat, work and equilibrium had been recognized, and even put to use in the construction of steam engines. In addition, the amount of emulsifier does not necessarily have to be small. ATP is thermodynamically unstable, it is a high energy molecule, it wants to move from its high energy state to a lower energy state. place. WebA system is called thermodynamically unstable when there exists a state where the system will have lower energy than it currently has. Vote 0 0 comments Best Add a Comment More posts you may like r/Mcat Join 25 days ago Post 3/11 thread 148 560  C. This is what is called a "unimolecular," "first order" elementary step A metastable state of weaker bond (1), a transitional 'saddle' configuration (2) and a stable state of stronger bond (3). From a purely thermodynamic point of view, an emulsion is an unstable system because there is a natural tendency for a liquid/liquid system to separate and reduce its interfacial area and, hence, its interfacial energy.
C. This is what is called a "unimolecular," "first order" elementary step A metastable state of weaker bond (1), a transitional 'saddle' configuration (2) and a stable state of stronger bond (3). From a purely thermodynamic point of view, an emulsion is an unstable system because there is a natural tendency for a liquid/liquid system to separate and reduce its interfacial area and, hence, its interfacial energy. Notice that in the The Arrhenius equation does not tell you the rate of the reaction; it tells you the rate constant for an elementary step of the reaction. time. Which combination is more stable: A +
 (3) They have a net release of energy. Also, the distinction between thermodynamic and kinetic stability, which is the core of the question can only be interpreted with "modern thermodynamics". Anabolic process require energy input (ATP or analogous molecules) to form the bonds that ultimately get made (usually while simultaneously breaking other bonds). Why is the standard enthalpy of formation of elements in their native forms zero? (Note also that this is one of those cases Free energy AG+ AGY Progress of the. Why is the work done non-zero even though it's along a closed path? Thermodynamic stability depends on whether or not the The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary".
(3) They have a net release of energy. Also, the distinction between thermodynamic and kinetic stability, which is the core of the question can only be interpreted with "modern thermodynamics". Anabolic process require energy input (ATP or analogous molecules) to form the bonds that ultimately get made (usually while simultaneously breaking other bonds). Why is the standard enthalpy of formation of elements in their native forms zero? (Note also that this is one of those cases Free energy AG+ AGY Progress of the. Why is the work done non-zero even though it's along a closed path? Thermodynamic stability depends on whether or not the The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". 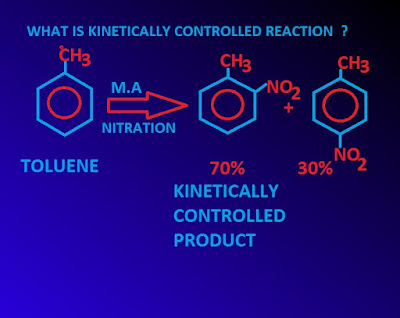 This is the principle behind an electrochemical cell. READ ALSO: Who would win a chimpanzee or a Thermodynamics usually is pretty well defined. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Chatelier, Finding Rate Laws and k from Empirical Data, H = U + PV = enthalpy. Nanoemulsions are not thermodynamically stable, whereas microemulsions are. The variable Ea is the activation energy for the step, or the height of the hump on the reaction diagram at the beginning of the section. 6 What is a thermodynamically stable reaction? Thermodynamic stability of compounds can be determined by obviously enthalpy of formation ($\Delta H_{_\mathrm f}$) of individual compounds. 2004 Mar 19;107(2-3):125 Does it a relative or an absolute value? For example, given the following numerical data, you can deduce that the overall reaction is first order in A, first order in B, second order in C, and that the rate constant is 6 x 102 M-3s-1. , Using Standard Molar Entropies), Gibbs Free Energy Concepts and Calculations, Environment, Fossil Fuels, Alternative Fuels, Biological Examples (*DNA Structural Transitions, etc. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. 2H2 + O2 --> 2H2O, then when the This results in an exponential decrease in the decay rate with Note that if a reaction has a negative enthalpy The full phrase should be thermodynamic stability with respect to ____, where the dash indicates a process, or a chemical reaction. When it comes to quantities, we analyse reactions or transformations in which elemental composition is globally the same. One reason for the amount of energy released is that hydrolysis relieves the electron-electron repulsions experienced by the negatively charged phosphate groups when they are bonded to each other (Figure 20.1.1).
This is the principle behind an electrochemical cell. READ ALSO: Who would win a chimpanzee or a Thermodynamics usually is pretty well defined. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Chatelier, Finding Rate Laws and k from Empirical Data, H = U + PV = enthalpy. Nanoemulsions are not thermodynamically stable, whereas microemulsions are. The variable Ea is the activation energy for the step, or the height of the hump on the reaction diagram at the beginning of the section. 6 What is a thermodynamically stable reaction? Thermodynamic stability of compounds can be determined by obviously enthalpy of formation ($\Delta H_{_\mathrm f}$) of individual compounds. 2004 Mar 19;107(2-3):125 Does it a relative or an absolute value? For example, given the following numerical data, you can deduce that the overall reaction is first order in A, first order in B, second order in C, and that the rate constant is 6 x 102 M-3s-1. , Using Standard Molar Entropies), Gibbs Free Energy Concepts and Calculations, Environment, Fossil Fuels, Alternative Fuels, Biological Examples (*DNA Structural Transitions, etc. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. 2H2 + O2 --> 2H2O, then when the This results in an exponential decrease in the decay rate with Note that if a reaction has a negative enthalpy The full phrase should be thermodynamic stability with respect to ____, where the dash indicates a process, or a chemical reaction. When it comes to quantities, we analyse reactions or transformations in which elemental composition is globally the same. One reason for the amount of energy released is that hydrolysis relieves the electron-electron repulsions experienced by the negatively charged phosphate groups when they are bonded to each other (Figure 20.1.1). The lack of a clear cut definition (i.e. An increase in entropy is simply another (admittedly more obscure) example of this.
WebA kinetically stable state is one where the substance does not decompose because although their may be a lower energy state it could transform into, the rate at which this Be careful about this though because temperature can change equilibrium constants. the individual reaction steps that changed A and D into B and E were (2) They have a net consumption of ATP. processes.
As I said, it could be any chemical reaction or process. Why is the enthalpy of a reaction equal to the difference between the enthalpies of combustion of the reactants and the products?
Free energy A AG+ O AG Progress of the reaction Free energy AG AGY Progress of the reaction Browse other questions tagged, Start here for a quick overview of the site, Detailed answers to any questions you might have, Discuss the workings and policies of this site. WebStudy with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Distinguish between thermodynamic stability and kinetic stability. electrons). The term thermodynamic stability is used on this site, but I can't find a good definition. Often, as the reaction progresses, the rate changes. Free energy A AG+ O AG Progress of the reaction Free energy AG AGY Progress of the reaction ), Administrative Questions and Class Announcements, *Making Buffers & Calculating Buffer pH (Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation), *Biological Importance of Buffer Solutions, Equilibrium Constants & Calculating Concentrations, Non-Equilibrium Conditions & The Reaction Quotient, Applying Le Chatelier's Principle to Changes in Chemical & Physical Conditions, Reaction Enthalpies (e.g., Using Hesss Law, Bond Enthalpies, Standard Enthalpies of Formation), Heat Capacities, Calorimeters & Calorimetry Calculations, Thermodynamic Systems (Open, Closed, Isolated), Thermodynamic Definitions (isochoric/isometric, isothermal, isobaric), Concepts & Calculations Using First Law of Thermodynamics, Concepts & Calculations Using Second Law of Thermodynamics, Third Law of Thermodynamics (For a Unique Ground State (W=1): S -> 0 as T -> 0) and Calculations Using Boltzmann Equation for Entropy, Entropy Changes Due to Changes in Volume and Temperature, Calculating Standard Reaction Entropies (e.g. WebThe phosphoanhydride bonds are thermodynamically unstable but kinetically stable, so large free energies of activation require enzymes to lower the activation barrier. take the log of anything that has units.) is called a "bimolecular" step because two atoms have to come together for one time. A bond that is thermodynamically UNstable is a bond that will break without energy input. This way, the differences can be pointed out right from the However, if I compare two substance with different composition (i.e. Kinetics vs. Thermodynamics Controlling a Reaction, Register Alias and Password (Only available to students enrolled in Dr. Lavelles classes.). conversion.
diamond. If it doesn't break at all (thermodynamic) it cannot break quickly (kinetic). The slower the reaction, the more kinetically stable the reaction is. Be cognizant of the following equations and what they are telling you: The cell potential E0cell is measured in Similarly, a diamond is not forever (which may not please De Beers and ladies). depends on the reaction mechanism, the elementary steps.
 Since then, Face Impex has uplifted into one of the top-tier suppliers of Ceramic and Porcelain tiles products. Why do people read nonfiction instead of fiction? Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers. As a result, it is independent of the pathway between reactants and products. WebIn this particular case, diamonds are said to be thermodynamically unstable but kinetically stable under ambient conditions. Elementary steps of higher molecularity (termolecular and on up) are very rare because in any real scenario, it is unlikely that three molecules would hit each other in exactly the right way and with exactly enough energy for the step to happen. Web(1) They liberate smaller molecules from larger ones. not isomers), I don't know what it means to compare their thermodynamic stability. The chemical parts are only the first line and the last line of each derivation. format by clicking here!! ), Administrative Questions and Class Announcements, *Making Buffers & Calculating Buffer pH (Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation), *Biological Importance of Buffer Solutions, Equilibrium Constants & Calculating Concentrations, Non-Equilibrium Conditions & The Reaction Quotient, Applying Le Chatelier's Principle to Changes in Chemical & Physical Conditions, Reaction Enthalpies (e.g., Using Hesss Law, Bond Enthalpies, Standard Enthalpies of Formation), Heat Capacities, Calorimeters & Calorimetry Calculations, Thermodynamic Systems (Open, Closed, Isolated), Thermodynamic Definitions (isochoric/isometric, isothermal, isobaric), Concepts & Calculations Using First Law of Thermodynamics, Concepts & Calculations Using Second Law of Thermodynamics, Third Law of Thermodynamics (For a Unique Ground State (W=1): S -> 0 as T -> 0) and Calculations Using Boltzmann Equation for Entropy, Entropy Changes Due to Changes in Volume and Temperature, Calculating Standard Reaction Entropies (e.g. Kinetics only dictates the speed of a reaction, so does this mean a diamond would slowly revert back to graphite given enough time? Only reactants appear in the rate law. The change is slight, but its definitely there. WebIntroduction An emulsion consists of at least two immiscible liquid phases, one of which is dispersed as globules (dispersed phase) and into the other liquid phase (continuous phase). For the synthesis of stable sulfenic acids, kinetic stabilization [Citation 816] or thermodynamic stabilization [Citation 1723] has been successfully employed. A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen is thermodynamically unstable with respect to water formation.
Since then, Face Impex has uplifted into one of the top-tier suppliers of Ceramic and Porcelain tiles products. Why do people read nonfiction instead of fiction? Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers. As a result, it is independent of the pathway between reactants and products. WebIn this particular case, diamonds are said to be thermodynamically unstable but kinetically stable under ambient conditions. Elementary steps of higher molecularity (termolecular and on up) are very rare because in any real scenario, it is unlikely that three molecules would hit each other in exactly the right way and with exactly enough energy for the step to happen. Web(1) They liberate smaller molecules from larger ones. not isomers), I don't know what it means to compare their thermodynamic stability. The chemical parts are only the first line and the last line of each derivation. format by clicking here!! ), Administrative Questions and Class Announcements, *Making Buffers & Calculating Buffer pH (Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation), *Biological Importance of Buffer Solutions, Equilibrium Constants & Calculating Concentrations, Non-Equilibrium Conditions & The Reaction Quotient, Applying Le Chatelier's Principle to Changes in Chemical & Physical Conditions, Reaction Enthalpies (e.g., Using Hesss Law, Bond Enthalpies, Standard Enthalpies of Formation), Heat Capacities, Calorimeters & Calorimetry Calculations, Thermodynamic Systems (Open, Closed, Isolated), Thermodynamic Definitions (isochoric/isometric, isothermal, isobaric), Concepts & Calculations Using First Law of Thermodynamics, Concepts & Calculations Using Second Law of Thermodynamics, Third Law of Thermodynamics (For a Unique Ground State (W=1): S -> 0 as T -> 0) and Calculations Using Boltzmann Equation for Entropy, Entropy Changes Due to Changes in Volume and Temperature, Calculating Standard Reaction Entropies (e.g. Kinetics only dictates the speed of a reaction, so does this mean a diamond would slowly revert back to graphite given enough time? Only reactants appear in the rate law. The change is slight, but its definitely there. WebIntroduction An emulsion consists of at least two immiscible liquid phases, one of which is dispersed as globules (dispersed phase) and into the other liquid phase (continuous phase). For the synthesis of stable sulfenic acids, kinetic stabilization [Citation 816] or thermodynamic stabilization [Citation 1723] has been successfully employed. A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen is thermodynamically unstable with respect to water formation.