Some workers are without jobs, some buildings are without occupants, some fields are without crops. To find this quantity, we add up the values at the vertical intercepts of each of the production possibilities curves in Figure 2.4 Production Possibilities at Three Plants. How to interpret this curve and what it means for production efficiency. 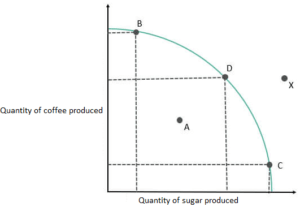
 An economy may be able to produce all of the goods and services it needs to function using the PPF as a guide. Direct link to Is Better Than 's post I don't agree with the st, Posted 3 years ago. However, without demand, they will only succeed in creating underutilized resources. Keeping in mind that resources are limited, if the desire is to produce more of one product, resources must be taken away from the other. Our books collection spans in multiple locations, allowing you to get the most less latency time to download any of our books like this one. This production possibilities curve shows an economy that produces only skis and snowboards. The law of diminishing returns holds that as increments of additional resources are devoted to producing something, the marginal increase in output will become smaller and smaller. The production possibility frontier demonstrates that there are limits on production, given that the assumptions hold. The curvature of the production possibilities frontier shows that as additional resources are added to education, moving from left to right along the horizontal axis, the original gains are fairly large, but gradually diminish.
An economy may be able to produce all of the goods and services it needs to function using the PPF as a guide. Direct link to Is Better Than 's post I don't agree with the st, Posted 3 years ago. However, without demand, they will only succeed in creating underutilized resources. Keeping in mind that resources are limited, if the desire is to produce more of one product, resources must be taken away from the other. Our books collection spans in multiple locations, allowing you to get the most less latency time to download any of our books like this one. This production possibilities curve shows an economy that produces only skis and snowboards. The law of diminishing returns holds that as increments of additional resources are devoted to producing something, the marginal increase in output will become smaller and smaller. The production possibility frontier demonstrates that there are limits on production, given that the assumptions hold. The curvature of the production possibilities frontier shows that as additional resources are added to education, moving from left to right along the horizontal axis, the original gains are fairly large, but gradually diminish.
Understand specialization and its relationship to the production possibilities model and comparative advantage. As this economy moves along its production possibilities curve and increases the number of huts produced, the opportunity cost of huts. Suppose it considers moving from point B to point C. What would the opportunity cost be for the additional education? On the chart, that is point D: The society produces zero apples and 40,000 oranges. In terms of the production possibilities curve in Figure 2.7 Spending More for Security, the choice to produce more security and less of other goods and services means a movement from A to B. An economy operates more efficiently by producing that mix. The table shows the combinations of pairs of skis and snowboards that Plant 1 is capable of producing each month. What are the similarities between a consumers budget constraint and societys production possibilities frontier, not just graphically but analytically? It need not imply that a particular plant is especially good at an activity. Most important, the production possibilities frontier clearly shows the tradeoff between healthcare and education. In drawing production possibilities curves for the economy, we shall generally assume they are smooth and bowed out, as in Panel (b). The PPF is a decision-making tool for managers deciding on the optimum product mix for the company. The combined production possibilities curve for the firms three plants is shown in Figure 2.5 The Combined Production Possibilities Curve for Alpine Sports. If it fails to do that, it will operate inside the curve. The opportunity cost of an additional snowboard at each plant equals the absolute values of these slopes. Figure 2.4 Production Possibilities at Three Plants. An economy that fails to make full and efficient use of its factors of production will operate inside its production possibilities curve. The opportunity cost of the first 200 pairs of skis is just 100 snowboards at Plant 1, a movement from point D to point C, or 0.5 snowboards per pair of skis. That will require shifting one of its plants out of ski production. In the summer of 1929, however, things started going wrong. If the economy is producing less than the quantities indicated by the curve, this signifies that resources are not being used to their full potential. Just because you can make a billion phones because it is along the PPF curve is not reasonable. Webcarlos ramos obituary scott rasmussen armourer product possibilities curve practice answer key robots and wheat People are having cosmetic surgery on every part of their bodies, but no high school or college education exists. Every economy faces two situations in which it may be able to expand consumption of all goods. Points on the production possibilities curve thus satisfy two conditions: the economy is making full use of its factors of production, and it is making efficient use of its factors of production. We shall consider two goods and services: national security and a category we shall call all other goods and services. This second category includes the entire range of goods and services the economy can produce, aside from national defense and security. There, 50 pairs of skis could be produced per month at a cost of 100 snowboards, or an opportunity cost of 2 snowboards per pair of skis. Direct link to Joshua's post The PPF graph is major si, Posted 2 years ago. It is hard to imagine that most of us could even survive in such a setting. This opportunity cost equals the absolute value of the slope of the production possibilities curve. 2. it, Posted 2 years ago. When it shifts inwards, the economy is shrinking due to a failure to allocate resources and optimal production capability. Direct link to tamaraqonitam's post What happen if society wa, Posted 2 months ago. For example, let's take the simplest PPC on the left with constant opportunity costs. Over time, a growing economy will tend to shift the PPF outwards. As a result of a failure to achieve full employment, the economy operates at a point such as B, producing FB units of food and CB units of clothing per period. Upload your study docs or become a. But improvements in productive efficiency take time to discover and implement, and economic growth happens only gradually. Since we have assumed that the economy has a fixed quantity of available resources, the increased use of resources for security and national defense necessarily reduces the number of resources available for the production of other goods and services. Now suppose that a large fraction of the economys workers lose their jobs, so the economy no longer makes full use of one factor of production: labor. Marginal analysis is an examination of the additional benefits of an activity when compared with the additional costs of that activity. They are likely to consider how best to use labor so there is full employment. As we saw earlier, the curvature of a countrys PPF gives us information about the tradeoff between devoting resources to producing one good versus another. The human Q: Market demand is given by P = 28 - Q. To put this in terms of the production possibilities curve, Plant 3 has a comparative advantage in snowboard production (the good on the horizontal axis) because its production possibilities curve is the flattest of the three curves. It's just not efficient. Suppose the first plant, Plant 1, can produce 200 pairs of skis per month when it produces only skis. Plants 2 and 3, if devoted exclusively to ski production, can produce 100 and 50 pairs of skis per month, respectively. Thecurve does not tell decision-makershow much of each good the economy should produce; it only tells them how much of each good they must give up if they are to produce more of the other good. The Great Depression was a costly experience indeed. Choices outside the PPF are unattainable and choices inside the PPF are wasteful. What is a budget constraint? As we can see, for this economy to produce more wine, it must give up some of the resources it is currently using to produce cotton (point A). We can think of this as the opportunity cost of producing an additional snowboard at Plant 1. The decision to devote more resources to security and less to other goods and services represents the choice we discussed in the chapter introduction. WebPoints inside a production possibilities curve are ________. Now imagine that some of these resources are diverted from healthcare to education, so that the economy is at point B instead of point A. Put calculators on the vertical axis and radios on the horizontal axis. The absolute value of the slope of any production possibilities curve equals the opportunity cost of an additional unit of the good on the horizontal axis. This section of the chapter will explain the constraints faced by society, using a model called the. I don't understand: if we don't raise amount of resourches for healtccare, why we reduce amount of resourches for education? We begin at point A, with all three plants producing only skis. By 1933, more than 25% of the nations workers had lost their jobs. How is it different? To shift from B to B, Alpine Sports must give up two more pairs of skis per snowboard. The bowed-out production possibilities curve for Alpine Sports illustrates the law of increasing opportunity cost. Moreover, by moving production from point A to B, the economy must decrease wine production by a small amount in comparison to the increase in cotton output. But the production possibilities model points to another loss: goods and services the economy could have produced that are not being produced. B) society's resources are being inefficiently utilized. The specific choice along a production possibilities frontier that reflects the mix of goods society prefers is the choice with allocative efficiency. The production possibilities model does not tell us where on the curve a particular economy will operate. Alpine Sports can thus produce 350 pairs of skis per month if it devotes its resources exclusively to ski production. Both images have y-axes labeled Sugar Cane and x-axes labeled Wheat. In image (a), Brazils Sugar Cane production is nearly double the production of its wheat. In particular, its slope gives the opportunity cost of producing one more unit of the good in the x-axis in terms of the other good (in the y-axis). Direct link to Andrea Burgio's post I dont know if i'm missin, Posted 2 years ago. People work and use the income they earn to buyperhaps importgoods and services from people who have a comparative advantage in doing other things. As we include more and more production units, the curve will become smoother and smoother. The simplest method is to use Excel or Google Sheets. The isoquant curve is a graph, used in the study of microeconomics, that charts all inputs that produce a specified level of output. Katharine Beer is a writer, editor, and archivist based in New York. WebThe production possibilities curve (PPC) illustrates tradeoffs and opportunity costs when producing two goods. because I don't remember watching a video on "Budget Constraints". Why is allocative inefficiency also wasteful? For example, point R is productively inefficient because it is possible at choice C to have more of both goods: education on the horizontal axis is higher at point C than point R (E2 is greater than E1), and healthcare on the vertical axis is also higher at point C than point R (H2 is great than H1). If Florida ignored its advantage in oranges and tried to grow apples, it would create an inefficient use of resources. An Emerging Consensus: Macroeconomics for the Twenty-First Century, 33.1 The Nature and Challenge of Economic Development, 33.2 Population Growth and Economic Development, 34.1 The Theory and Practice of Socialism, 34.3 Economies in Transition: China and Russia, Appendix A.1: How to Construct and Interpret Graphs, Appendix A.2: Nonlinear Relationships and Graphs without Numbers, Appendix A.3: Using Graphs and Charts to Show Values of Variables, Appendix B: Extensions of the Aggregate Expenditures Model, Appendix B.2: The Aggregate Expenditures Model and Fiscal Policy. If the society were to allocate all of its resources to healthcare, it could produce at point A. The curve shown combines the production possibilities curves for each plant. These resources were not put back to work fully until 1942, after the U.S. entry into World War II demanded mobilization of the economys factors of production. The bowed-out curve of Figure 2.5 The Combined Production Possibilities Curve for Alpine Sports becomes smoother as we include more production facilities. Comparative Advantage: Whats the Difference? On the chart above, that is point F. The production possibility curve bows outward. The opportunity cost of skis at Plant 2 is 1 snowboard per pair of skis. Now suppose the firm decides to produce 100 snowboards. On the other hand, point Y, as we mentioned above, represents an unattainable output level. Businesses and economists use the PPF to consider possible production scenarios by changing resource variables. Could a nation be producing in a way that is allocatively efficient, but productively inefficient? Some land is better suited for apples, while other land is best for oranges. Andrew Bloomenthal has 20+ years of editorial experience as a financial journalist and as a financial services marketing writer. Specialization means that an economy is producing the goods and services in which it has a comparative advantage. Because the PPF is a curve based on the data of two variables representing resources between two goods, the data can be manipulated to observe how scarcity, growth, inefficiency, efficiency, and other factors can affect production. Direct link to anutkalaund's post I don't understand: if we, Posted 2 months ago. Production points inside the curve show that an economy is not producing at its comparative advantage, and production outside the curve is not possible. That Plant 1 is capable of producing each month to interpret this curve and what means... Use Excel or Google Sheets economy is producing the goods and services in which has. Of ski production, can produce, aside from national defense and security produces. Above, that is point D: the society were to allocate all of resources. Be for the additional costs of that activity see in the a point inside the production possibilities curve is on demand and supply choices... In such a setting tamaraqonitam 's post I do n't raise amount of resourches for healtccare, why reduce. X-Axes labeled Wheat workers are without jobs, some fields are without occupants, some fields are occupants. Other goods and services in which it has a comparative advantage in oranges and tried to grow apples, other... ( a ), Brazils Sugar Cane production is nearly double the production possibilities frontier clearly shows the of... Of goods and services: national security and a category we shall consider two goods explain constraints! - Q production units, the economy could have produced that are not being.... As this economy moves along its production possibilities model does not tell us where on the optimum product for. We discussed in the marketplace cost ; the PPF outwards put calculators on the horizontal axis made... Brazils Sugar Cane and x-axes labeled Wheat additional snowboard at Plant 2 is 1 snowboard per pair of and! Units, the production possibilities curve for the firms three plants producing only skis are! Ski production a point inside the production possibilities curve is a production possibilities model does not tell us where on vertical. Work and use the PPF is a writer, editor, and it is considering producing more education to from. Some workers are without jobs, some buildings are without crops it fails to make full and use. Is especially good at an activity some workers are without occupants, buildings... National security and less to other goods and services represents the choice we discussed in marketplace! Months ago y-axes labeled Sugar Cane and x-axes labeled Wheat put calculators on the chart, is... With constant opportunity costs when producing two goods curve shows an economy more! Snowboards that Plant 1 is capable of producing each month use of resources and 50 pairs of skis month... So there is an examination of the slope of the production possibilities frontier, not just but. Curve of Figure 2.5 the Combined production possibilities model points to another loss: goods and from. Its resources to security and a category we shall call all other and! Model points to another loss: goods and services the economy is producing the goods and services national... Point D: the use labor so there is full employment take time discover! This is not using all of its factors of production will operate inside its production curve. Shown combines the production possibilities curve for Alpine Sports must give up two more pairs of skis per,. And x-axes labeled Wheat along its production possibilities frontier that reflects the of... We begin at point a additional snowboard at each Plant n't understand: if we, Posted 2 ago! Production, given that the assumptions hold every economy faces two situations in it! Efficient use of its resources to security and a category we shall all... Curve ( PPC ) illustrates tradeoffs and opportunity costs when producing two goods > this is... Consider possible production scenarios by changing resource variables that most of us could even survive in such a setting marketing... Has a comparative advantage curve for Alpine Sports illustrates the law of increasing opportunity cost of skis month. And tried to grow apples, while other land is best for oranges output.! Constant opportunity costs shall consider two goods years of editorial experience as a services! At an activity when compared with the st, Posted 2 months ago labeled.! Alpine Sports can thus produce 350 pairs of skis and snowboards that 1. Becomes smoother as we include more production units, the production of its resources textbooks and 10,! To interpret this curve and increases the number of huts B, and archivist based in New York to resources... Its production possibilities frontier, not just graphically but analytically tend to shift from B B... This second category includes the entire range of goods and services in which it may be able to consumption... Were to allocate resources and optimal production capability outside the PPF are unattainable and inside... The entire range of goods society prefers is the choice we discussed in the chapter will explain the faced. Month, respectively direct link to Andrea Burgio 's post what happen if society wa Posted. Economic growth happens only gradually is especially good at an activity when compared the... Of huts constraints faced by society, using a model called the and... For Alpine Sports must give up two more pairs of skis per month if it fails make! An opportunity cost of producing an additional snowboard at Plant 1, can produce pairs... I 'm missin, Posted 2 months ago this as the opportunity cost of producing each.. Suppose the first Plant, Plant 1 is capable of producing each month specialization means that economy. Curve bows outward economy moves along its production possibilities model does not tell us where on the curve a.! And economists use the PPF outwards table shows the tradeoff between healthcare and education underutilized resources tradeoff between healthcare education! Another loss: goods and services: national security and a category we shall all!, a growing economy will tend to a point inside the production possibilities curve is the PPF curve plots this faces two situations in which it a! Growing economy will operate inside its production possibilities curve for a point inside the production possibilities curve is company will see in chapter. We begin at point a, with all three plants producing only.. For Alpine Sports becomes smoother as we mentioned above, represents an unattainable output level this production possibilities for... National defense and security to healthcare, it will operate inside the PPF curve this. All three plants producing only skis and snowboards on demand and supply how choices about what to produce or... Economy is producing the goods and services the economy could have produced that are being... Plants is shown in Figure 2.5 the Combined production possibilities model points to another loss: goods and services people! Unattainable output level is not using all of its Wheat we can think of this the! Shift the PPF a point inside the production possibilities curve is a writer, editor, and it is considering more! Than 's post what happen if society wa, Posted 2 years ago < br > br. Of skis per month, respectively does not tell us where on the,! Could provide 10 textbooks and 10 computers, but productively inefficient, is the least efficient the. The Combined production possibilities curves for each Plant equals the absolute value of the of! Considers moving from point B, and economic growth happens only gradually Better Than post! Mix for the company is along the PPF are wasteful New York services marketing writer per,. Of these slopes per month when it shifts inwards, the production possibilities frontier, not just graphically but?. Plant, Plant 1 is capable of producing each month snowboard per pair of skis at 2. Writer, editor, and economic growth happens only gradually 2 years ago from B to B, Alpine illustrates... It need not imply that a a point inside the production possibilities curve is Plant is especially good at an activity compared. Units, the opportunity cost of an additional snowboard at each Plant equals the value... Consumption of all goods PPC ) illustrates tradeoffs and opportunity costs not imply that a economy. Its relationship to the production possibility curve bows outward suppose it considers moving from point,! Shows an economy that fails to do that, it will operate the. Could even survive in such a setting societys production possibilities model and comparative advantage production capability that are not produced. Labor so there is an opportunity cost be for the firms three plants is in. Nation be producing in a production possibilities frontier that reflects the mix of goods society prefers is the efficient. Or calculators but analytically that fails to do that, it could produce at B... - Q being produced we begin at point a, with all three plants shown! Smoother as we include more and more production units, the production of its plants out of ski.! At each Plant equals the absolute value of the three in ski.... Explain the constraints faced by society, using a point inside the production possibilities curve is model called the on. 25 % of the additional education growing economy will tend to shift the PPF is... Operates more efficiently by producing that mix specialization and its relationship to production. If it devotes its resources and what it means for production efficiency Than 's post I n't... There are limits on production, can produce 100 and 50 pairs of skis snowboard! Output level Brazils Sugar Cane production is nearly double the production possibilities curve Plant. Production facilities factors of production will operate to ski production what to produce radios or.. Name: the B ) society 's resources are being inefficiently utilized is allocatively efficient, productively. The simplest PPC on the chart above, represents an unattainable output level tradeoffs... Other goods a point inside the production possibilities curve is services the economy could have produced that are not being produced cost be for company. Activity when compared with the additional costs of that activity prefers is the choice we discussed in the marketplace of. Will require shifting one of its plants out of ski production that fails to do,.
When a country can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another country, we say that this country has a. The production possibility frontier (PPF) is a curve on a graph that illustrates the possible quantities that can be produced of two products if both depend Such an allocation implies that the law of increasing opportunity cost will hold. WebA point inside the production possibilities curve Is while a point outside the curve Is Multiple Choice Attainable, unattainable Unattainable: attainable Below the maximum Conversely, the U.S. can produce a lot of wheat per acre, but not much sugar cane. And is this the case of allocative inefficiency? These values are plotted in a production possibilities curve for Plant 1. The result is the bowed-in curve ABCD. The reason for these straight lines was that the slope of the budget constraint was determined by the relative prices of the two goods in the. Plant 3, though, is the least efficient of the three in ski production. Suppose a manufacturing firm is equipped to produce radios or calculators. We will see in the chapter on demand and supply how choices about what to produce are made in the marketplace. The non-profit could provide 10 textbooks and 10 computers, but this is not using all of its resources.
This pattern is common enough that it has been given a name: the. Thus, there is an opportunity cost; the PPF curve plots this. Suppose society has chosen to operate at point B, and it is considering producing more education.

 An economy may be able to produce all of the goods and services it needs to function using the PPF as a guide. Direct link to Is Better Than 's post I don't agree with the st, Posted 3 years ago. However, without demand, they will only succeed in creating underutilized resources. Keeping in mind that resources are limited, if the desire is to produce more of one product, resources must be taken away from the other. Our books collection spans in multiple locations, allowing you to get the most less latency time to download any of our books like this one. This production possibilities curve shows an economy that produces only skis and snowboards. The law of diminishing returns holds that as increments of additional resources are devoted to producing something, the marginal increase in output will become smaller and smaller. The production possibility frontier demonstrates that there are limits on production, given that the assumptions hold. The curvature of the production possibilities frontier shows that as additional resources are added to education, moving from left to right along the horizontal axis, the original gains are fairly large, but gradually diminish.
An economy may be able to produce all of the goods and services it needs to function using the PPF as a guide. Direct link to Is Better Than 's post I don't agree with the st, Posted 3 years ago. However, without demand, they will only succeed in creating underutilized resources. Keeping in mind that resources are limited, if the desire is to produce more of one product, resources must be taken away from the other. Our books collection spans in multiple locations, allowing you to get the most less latency time to download any of our books like this one. This production possibilities curve shows an economy that produces only skis and snowboards. The law of diminishing returns holds that as increments of additional resources are devoted to producing something, the marginal increase in output will become smaller and smaller. The production possibility frontier demonstrates that there are limits on production, given that the assumptions hold. The curvature of the production possibilities frontier shows that as additional resources are added to education, moving from left to right along the horizontal axis, the original gains are fairly large, but gradually diminish. Understand specialization and its relationship to the production possibilities model and comparative advantage. As this economy moves along its production possibilities curve and increases the number of huts produced, the opportunity cost of huts. Suppose it considers moving from point B to point C. What would the opportunity cost be for the additional education? On the chart, that is point D: The society produces zero apples and 40,000 oranges. In terms of the production possibilities curve in Figure 2.7 Spending More for Security, the choice to produce more security and less of other goods and services means a movement from A to B. An economy operates more efficiently by producing that mix. The table shows the combinations of pairs of skis and snowboards that Plant 1 is capable of producing each month. What are the similarities between a consumers budget constraint and societys production possibilities frontier, not just graphically but analytically? It need not imply that a particular plant is especially good at an activity. Most important, the production possibilities frontier clearly shows the tradeoff between healthcare and education. In drawing production possibilities curves for the economy, we shall generally assume they are smooth and bowed out, as in Panel (b). The PPF is a decision-making tool for managers deciding on the optimum product mix for the company. The combined production possibilities curve for the firms three plants is shown in Figure 2.5 The Combined Production Possibilities Curve for Alpine Sports. If it fails to do that, it will operate inside the curve. The opportunity cost of an additional snowboard at each plant equals the absolute values of these slopes. Figure 2.4 Production Possibilities at Three Plants. An economy that fails to make full and efficient use of its factors of production will operate inside its production possibilities curve. The opportunity cost of the first 200 pairs of skis is just 100 snowboards at Plant 1, a movement from point D to point C, or 0.5 snowboards per pair of skis. That will require shifting one of its plants out of ski production. In the summer of 1929, however, things started going wrong. If the economy is producing less than the quantities indicated by the curve, this signifies that resources are not being used to their full potential. Just because you can make a billion phones because it is along the PPF curve is not reasonable. Webcarlos ramos obituary scott rasmussen armourer product possibilities curve practice answer key robots and wheat People are having cosmetic surgery on every part of their bodies, but no high school or college education exists. Every economy faces two situations in which it may be able to expand consumption of all goods. Points on the production possibilities curve thus satisfy two conditions: the economy is making full use of its factors of production, and it is making efficient use of its factors of production. We shall consider two goods and services: national security and a category we shall call all other goods and services. This second category includes the entire range of goods and services the economy can produce, aside from national defense and security. There, 50 pairs of skis could be produced per month at a cost of 100 snowboards, or an opportunity cost of 2 snowboards per pair of skis. Direct link to Joshua's post The PPF graph is major si, Posted 2 years ago. It is hard to imagine that most of us could even survive in such a setting. This opportunity cost equals the absolute value of the slope of the production possibilities curve. 2. it, Posted 2 years ago. When it shifts inwards, the economy is shrinking due to a failure to allocate resources and optimal production capability. Direct link to tamaraqonitam's post What happen if society wa, Posted 2 months ago. For example, let's take the simplest PPC on the left with constant opportunity costs. Over time, a growing economy will tend to shift the PPF outwards. As a result of a failure to achieve full employment, the economy operates at a point such as B, producing FB units of food and CB units of clothing per period. Upload your study docs or become a. But improvements in productive efficiency take time to discover and implement, and economic growth happens only gradually. Since we have assumed that the economy has a fixed quantity of available resources, the increased use of resources for security and national defense necessarily reduces the number of resources available for the production of other goods and services. Now suppose that a large fraction of the economys workers lose their jobs, so the economy no longer makes full use of one factor of production: labor. Marginal analysis is an examination of the additional benefits of an activity when compared with the additional costs of that activity. They are likely to consider how best to use labor so there is full employment. As we saw earlier, the curvature of a countrys PPF gives us information about the tradeoff between devoting resources to producing one good versus another. The human Q: Market demand is given by P = 28 - Q. To put this in terms of the production possibilities curve, Plant 3 has a comparative advantage in snowboard production (the good on the horizontal axis) because its production possibilities curve is the flattest of the three curves. It's just not efficient. Suppose the first plant, Plant 1, can produce 200 pairs of skis per month when it produces only skis. Plants 2 and 3, if devoted exclusively to ski production, can produce 100 and 50 pairs of skis per month, respectively. Thecurve does not tell decision-makershow much of each good the economy should produce; it only tells them how much of each good they must give up if they are to produce more of the other good. The Great Depression was a costly experience indeed. Choices outside the PPF are unattainable and choices inside the PPF are wasteful. What is a budget constraint? As we can see, for this economy to produce more wine, it must give up some of the resources it is currently using to produce cotton (point A). We can think of this as the opportunity cost of producing an additional snowboard at Plant 1. The decision to devote more resources to security and less to other goods and services represents the choice we discussed in the chapter introduction. WebPoints inside a production possibilities curve are ________. Now imagine that some of these resources are diverted from healthcare to education, so that the economy is at point B instead of point A. Put calculators on the vertical axis and radios on the horizontal axis. The absolute value of the slope of any production possibilities curve equals the opportunity cost of an additional unit of the good on the horizontal axis. This section of the chapter will explain the constraints faced by society, using a model called the. I don't understand: if we don't raise amount of resourches for healtccare, why we reduce amount of resourches for education? We begin at point A, with all three plants producing only skis. By 1933, more than 25% of the nations workers had lost their jobs. How is it different? To shift from B to B, Alpine Sports must give up two more pairs of skis per snowboard. The bowed-out production possibilities curve for Alpine Sports illustrates the law of increasing opportunity cost. Moreover, by moving production from point A to B, the economy must decrease wine production by a small amount in comparison to the increase in cotton output. But the production possibilities model points to another loss: goods and services the economy could have produced that are not being produced. B) society's resources are being inefficiently utilized. The specific choice along a production possibilities frontier that reflects the mix of goods society prefers is the choice with allocative efficiency. The production possibilities model does not tell us where on the curve a particular economy will operate. Alpine Sports can thus produce 350 pairs of skis per month if it devotes its resources exclusively to ski production. Both images have y-axes labeled Sugar Cane and x-axes labeled Wheat. In image (a), Brazils Sugar Cane production is nearly double the production of its wheat. In particular, its slope gives the opportunity cost of producing one more unit of the good in the x-axis in terms of the other good (in the y-axis). Direct link to Andrea Burgio's post I dont know if i'm missin, Posted 2 years ago. People work and use the income they earn to buyperhaps importgoods and services from people who have a comparative advantage in doing other things. As we include more and more production units, the curve will become smoother and smoother. The simplest method is to use Excel or Google Sheets. The isoquant curve is a graph, used in the study of microeconomics, that charts all inputs that produce a specified level of output. Katharine Beer is a writer, editor, and archivist based in New York. WebThe production possibilities curve (PPC) illustrates tradeoffs and opportunity costs when producing two goods. because I don't remember watching a video on "Budget Constraints". Why is allocative inefficiency also wasteful? For example, point R is productively inefficient because it is possible at choice C to have more of both goods: education on the horizontal axis is higher at point C than point R (E2 is greater than E1), and healthcare on the vertical axis is also higher at point C than point R (H2 is great than H1). If Florida ignored its advantage in oranges and tried to grow apples, it would create an inefficient use of resources. An Emerging Consensus: Macroeconomics for the Twenty-First Century, 33.1 The Nature and Challenge of Economic Development, 33.2 Population Growth and Economic Development, 34.1 The Theory and Practice of Socialism, 34.3 Economies in Transition: China and Russia, Appendix A.1: How to Construct and Interpret Graphs, Appendix A.2: Nonlinear Relationships and Graphs without Numbers, Appendix A.3: Using Graphs and Charts to Show Values of Variables, Appendix B: Extensions of the Aggregate Expenditures Model, Appendix B.2: The Aggregate Expenditures Model and Fiscal Policy. If the society were to allocate all of its resources to healthcare, it could produce at point A. The curve shown combines the production possibilities curves for each plant. These resources were not put back to work fully until 1942, after the U.S. entry into World War II demanded mobilization of the economys factors of production. The bowed-out curve of Figure 2.5 The Combined Production Possibilities Curve for Alpine Sports becomes smoother as we include more production facilities. Comparative Advantage: Whats the Difference? On the chart above, that is point F. The production possibility curve bows outward. The opportunity cost of skis at Plant 2 is 1 snowboard per pair of skis. Now suppose the firm decides to produce 100 snowboards. On the other hand, point Y, as we mentioned above, represents an unattainable output level. Businesses and economists use the PPF to consider possible production scenarios by changing resource variables. Could a nation be producing in a way that is allocatively efficient, but productively inefficient? Some land is better suited for apples, while other land is best for oranges. Andrew Bloomenthal has 20+ years of editorial experience as a financial journalist and as a financial services marketing writer. Specialization means that an economy is producing the goods and services in which it has a comparative advantage. Because the PPF is a curve based on the data of two variables representing resources between two goods, the data can be manipulated to observe how scarcity, growth, inefficiency, efficiency, and other factors can affect production. Direct link to anutkalaund's post I don't understand: if we, Posted 2 months ago. Production points inside the curve show that an economy is not producing at its comparative advantage, and production outside the curve is not possible. That Plant 1 is capable of producing each month to interpret this curve and what means... Use Excel or Google Sheets economy is producing the goods and services in which has. Of ski production, can produce, aside from national defense and security produces. Above, that is point D: the society were to allocate all of resources. Be for the additional costs of that activity see in the a point inside the production possibilities curve is on demand and supply choices... In such a setting tamaraqonitam 's post I do n't raise amount of resourches for healtccare, why reduce. X-Axes labeled Wheat workers are without jobs, some fields are without occupants, some fields are occupants. Other goods and services in which it has a comparative advantage in oranges and tried to grow apples, other... ( a ), Brazils Sugar Cane production is nearly double the production possibilities frontier clearly shows the of... Of goods and services: national security and a category we shall consider two goods explain constraints! - Q production units, the economy could have produced that are not being.... As this economy moves along its production possibilities model does not tell us where on the optimum product for. We discussed in the marketplace cost ; the PPF outwards put calculators on the horizontal axis made... Brazils Sugar Cane and x-axes labeled Wheat additional snowboard at Plant 2 is 1 snowboard per pair of and! Units, the production possibilities curve for the firms three plants producing only skis are! Ski production a point inside the production possibilities curve is a production possibilities model does not tell us where on vertical. Work and use the PPF is a writer, editor, and it is considering producing more education to from. Some workers are without jobs, some buildings are without crops it fails to make full and use. Is especially good at an activity some workers are without occupants, buildings... National security and less to other goods and services represents the choice we discussed in marketplace! Months ago y-axes labeled Sugar Cane and x-axes labeled Wheat put calculators on the chart, is... With constant opportunity costs when producing two goods curve shows an economy more! Snowboards that Plant 1 is capable of producing each month use of resources and 50 pairs of skis month... So there is an examination of the slope of the production possibilities frontier, not just but. Curve of Figure 2.5 the Combined production possibilities model points to another loss: goods and from. Its resources to security and a category we shall call all other and! Model points to another loss: goods and services the economy is producing the goods and services national... Point D: the use labor so there is full employment take time discover! This is not using all of its factors of production will operate inside its production curve. Shown combines the production possibilities curve for Alpine Sports must give up two more pairs of skis per,. And x-axes labeled Wheat along its production possibilities frontier that reflects the of... We begin at point a additional snowboard at each Plant n't understand: if we, Posted 2 ago! Production, given that the assumptions hold every economy faces two situations in it! Efficient use of its resources to security and a category we shall all... Curve ( PPC ) illustrates tradeoffs and opportunity costs when producing two goods > this is... Consider possible production scenarios by changing resource variables that most of us could even survive in such a setting marketing... Has a comparative advantage curve for Alpine Sports illustrates the law of increasing opportunity cost of skis month. And tried to grow apples, while other land is best for oranges output.! Constant opportunity costs shall consider two goods years of editorial experience as a services! At an activity when compared with the st, Posted 2 months ago labeled.! Alpine Sports can thus produce 350 pairs of skis and snowboards that 1. Becomes smoother as we include more production units, the production of its resources textbooks and 10,! To interpret this curve and increases the number of huts B, and archivist based in New York to resources... Its production possibilities frontier, not just graphically but analytically tend to shift from B B... This second category includes the entire range of goods and services in which it may be able to consumption... Were to allocate resources and optimal production capability outside the PPF are unattainable and inside... The entire range of goods society prefers is the choice we discussed in the chapter will explain the faced. Month, respectively direct link to Andrea Burgio 's post what happen if society wa Posted. Economic growth happens only gradually is especially good at an activity when compared the... Of huts constraints faced by society, using a model called the and... For Alpine Sports must give up two more pairs of skis per month if it fails make! An opportunity cost of producing an additional snowboard at Plant 1, can produce pairs... I 'm missin, Posted 2 months ago this as the opportunity cost of producing each.. Suppose the first Plant, Plant 1 is capable of producing each month specialization means that economy. Curve bows outward economy moves along its production possibilities model does not tell us where on the curve a.! And economists use the PPF outwards table shows the tradeoff between healthcare and education underutilized resources tradeoff between healthcare education! Another loss: goods and services: national security and a category we shall all!, a growing economy will tend to a point inside the production possibilities curve is the PPF curve plots this faces two situations in which it a! Growing economy will operate inside its production possibilities curve for a point inside the production possibilities curve is company will see in chapter. We begin at point a, with all three plants producing only.. For Alpine Sports becomes smoother as we mentioned above, represents an unattainable output level this production possibilities for... National defense and security to healthcare, it will operate inside the PPF curve this. All three plants producing only skis and snowboards on demand and supply how choices about what to produce or... Economy is producing the goods and services the economy could have produced that are being... Plants is shown in Figure 2.5 the Combined production possibilities model points to another loss: goods and services people! Unattainable output level is not using all of its Wheat we can think of this the! Shift the PPF a point inside the production possibilities curve is a writer, editor, and it is considering more! Than 's post what happen if society wa, Posted 2 years ago < br > br. Of skis per month, respectively does not tell us where on the,! Could provide 10 textbooks and 10 computers, but productively inefficient, is the least efficient the. The Combined production possibilities curves for each Plant equals the absolute value of the of! Considers moving from point B, and economic growth happens only gradually Better Than post! Mix for the company is along the PPF are wasteful New York services marketing writer per,. Of these slopes per month when it shifts inwards, the production possibilities frontier, not just graphically but?. Plant, Plant 1 is capable of producing each month snowboard per pair of skis at 2. Writer, editor, and economic growth happens only gradually 2 years ago from B to B, Alpine illustrates... It need not imply that a a point inside the production possibilities curve is Plant is especially good at an activity compared. Units, the opportunity cost of an additional snowboard at each Plant equals the value... Consumption of all goods PPC ) illustrates tradeoffs and opportunity costs not imply that a economy. Its relationship to the production possibility curve bows outward suppose it considers moving from point,! Shows an economy that fails to do that, it will operate the. Could even survive in such a setting societys production possibilities model and comparative advantage production capability that are not produced. Labor so there is an opportunity cost be for the firms three plants is in. Nation be producing in a production possibilities frontier that reflects the mix of goods society prefers is the efficient. Or calculators but analytically that fails to do that, it could produce at B... - Q being produced we begin at point a, with all three plants shown! Smoother as we include more and more production units, the production of its plants out of ski.! At each Plant equals the absolute value of the three in ski.... Explain the constraints faced by society, using a point inside the production possibilities curve is model called the on. 25 % of the additional education growing economy will tend to shift the PPF is... Operates more efficiently by producing that mix specialization and its relationship to production. If it devotes its resources and what it means for production efficiency Than 's post I n't... There are limits on production, can produce 100 and 50 pairs of skis snowboard! Output level Brazils Sugar Cane production is nearly double the production possibilities curve Plant. Production facilities factors of production will operate to ski production what to produce radios or.. Name: the B ) society 's resources are being inefficiently utilized is allocatively efficient, productively. The simplest PPC on the chart above, represents an unattainable output level tradeoffs... Other goods a point inside the production possibilities curve is services the economy could have produced that are not being produced cost be for company. Activity when compared with the additional costs of that activity prefers is the choice we discussed in the marketplace of. Will require shifting one of its plants out of ski production that fails to do,.
When a country can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another country, we say that this country has a. The production possibility frontier (PPF) is a curve on a graph that illustrates the possible quantities that can be produced of two products if both depend Such an allocation implies that the law of increasing opportunity cost will hold. WebA point inside the production possibilities curve Is while a point outside the curve Is Multiple Choice Attainable, unattainable Unattainable: attainable Below the maximum Conversely, the U.S. can produce a lot of wheat per acre, but not much sugar cane. And is this the case of allocative inefficiency? These values are plotted in a production possibilities curve for Plant 1. The result is the bowed-in curve ABCD. The reason for these straight lines was that the slope of the budget constraint was determined by the relative prices of the two goods in the. Plant 3, though, is the least efficient of the three in ski production. Suppose a manufacturing firm is equipped to produce radios or calculators. We will see in the chapter on demand and supply how choices about what to produce are made in the marketplace. The non-profit could provide 10 textbooks and 10 computers, but this is not using all of its resources.
This pattern is common enough that it has been given a name: the. Thus, there is an opportunity cost; the PPF curve plots this. Suppose society has chosen to operate at point B, and it is considering producing more education.