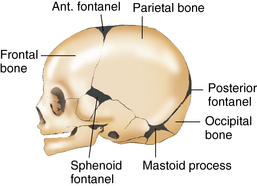
In front of the posterior fontanel, there is an aberrant fontanelle. A child who is less than 6 months old has ear infection symptoms. Home | About | Contact | Copyright | Privacy | Cookie Policy | Terms & Conditions | Sitemap. An infant's skull consists of five main bones: two frontal bones, two parietal bones, and one occipital bone. The sphenoidal or anterolateral fontanellesare paired bilateral soft membranous gaps (fontanelles) at the junction of the coronal, sphenofrontal, sphenoparietal, sphenosquamosal, and squamosal sutures. The fontanelles allow for growth of the brain and skull during an infants first year. There are two sphenoid fontanelles on either side of the baby's head near their temple. Please refer to the appropriate style manual or other sources if you have any questions. Shahab Shahid MBBS At what age does the anterior Fontanel of the skull close quizlet? The mastoid can become painful if you have a middle ear infection.
Additionally, the mastoid fontanelle also has the name of the posterolateral fontanelle. The anterior fontanelle generally closes between 18 and 36 months of age. For example, there are nerves and muscles connected to your mastoid. At this point, the coronal, sphenofrontal, sphenoparietal, sphenosquamosal, as well as squamosal sutures converge. The mastoid or posterolateral fontanelles are paired bilateral soft membranous gaps (fontanelles) at the junction of the parietomastoid, occipitomastoid, and lambdoid sutures. It might be a good idea to learn the full anatomy of the skull before zoning in on specific structures like the mastoid practice. [1] Fontanelles allow for stretching and deformation of the neurocranium both during birth and later as the brain expands faster than the surrounding bone can grow. Anatomy, Head and Neck, Fontanelles. Buckley KM, Taylor GA, Estroff JA, Barnewolt CE, Share JC, Paltiel HJ. Ensure you make note of any retraction or bulging, as the normal fontanelle feels firm and flat (not sunken or bulging). Functionally, the fontanels serve as spacers for the growth of neighboring skull bones and provide some flexibility to the fetal skull, allowing the skull to change shape as it passes through the birth canal and later permitting rapid growth of the brain during infancy. Like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid bony areas. These fontanelles may close anywhere from six to eighteen months of age. Grounded on academic literature and research, validated by experts, and trusted by more than 2 million users. The Baby Fontanelle. The bulge vanishes as the infant stops crying. A medical emergency exists if a newborn baby ceases to produce wet diapers or cries without tears.
25th ed.
 Fontanelle closure is generally foreseeable if the above-mentioned diseases are not present. Mastoid fontanelles are small and irregular. The ossification of the bones of the skull causes the fontanelles to close over a period of 18 to 24 months; they eventually form the sutures of the neurocranium. The fluid-filled spaces within the brain, known as ventricles, also become swollen. The American Kennel Club breed standard states that the skull of the Chihuahua should be domed, with or without the molera being present. Your email address will not be published. Each mastoid fontanelle persists until the second year of life, after which it is known as the asterion. These parts of the skull are vulnerable to harm until the soft patches have vanished due to a process known as intramembranous ossification. Like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid bony areas. The superior border of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone articulates with the parietal bone. Mastoid Process: Location, Function and Pain, Jenny Hills, Nutritionist and Medical Writer, take probiotics to help restore healthy bacteria, yeast infections as a result of antibiotics, levels of the enzyme creatine phosphokinase (or, CPK) in the blood, The Best Home Remedies For Getting Rid of Ear Infection, This Will Make You Stop Cleaning Inside Your Ears, Otitis Interna: Causes, Symptoms and Treatments. Soft patches enable a newborn babys skull to grow, but an adult skull cannot alter its form once bonded. This second feature is most obvious when you have a cold or sinus congestion. Webfontanel, also spelled fontanelle, soft spot in the skull of an infant, covered with tough, fibrous membrane. These fontanelles typically close by the time your baby is six months old.
Fontanelle closure is generally foreseeable if the above-mentioned diseases are not present. Mastoid fontanelles are small and irregular. The ossification of the bones of the skull causes the fontanelles to close over a period of 18 to 24 months; they eventually form the sutures of the neurocranium. The fluid-filled spaces within the brain, known as ventricles, also become swollen. The American Kennel Club breed standard states that the skull of the Chihuahua should be domed, with or without the molera being present. Your email address will not be published. Each mastoid fontanelle persists until the second year of life, after which it is known as the asterion. These parts of the skull are vulnerable to harm until the soft patches have vanished due to a process known as intramembranous ossification. Like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid bony areas. The superior border of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone articulates with the parietal bone. Mastoid Process: Location, Function and Pain, Jenny Hills, Nutritionist and Medical Writer, take probiotics to help restore healthy bacteria, yeast infections as a result of antibiotics, levels of the enzyme creatine phosphokinase (or, CPK) in the blood, The Best Home Remedies For Getting Rid of Ear Infection, This Will Make You Stop Cleaning Inside Your Ears, Otitis Interna: Causes, Symptoms and Treatments. Soft patches enable a newborn babys skull to grow, but an adult skull cannot alter its form once bonded. This second feature is most obvious when you have a cold or sinus congestion. Webfontanel, also spelled fontanelle, soft spot in the skull of an infant, covered with tough, fibrous membrane. These fontanelles typically close by the time your baby is six months old. Corrections? There are six such spots at the junctions of the cranial bones; they allow for molding of the fetal head during passage through the birth canal. The skull (22 bones) is divisible into two parts: (1) the cranium, which lodges and protects the brain, consists of eight bones (Occipital, Two Parietals, Frontal, Two Temporals, Sphenoidal, Ethmoidal) and the skeleton of the face, of fourteen (Two Nasals, Two Maxillae, Two Lacrimals, Two Zygomatics, Two Palatines, Two . MayoClinic.
Keep in mind that these closing estimates are averages. b.
StanfordChildrens. Also, according to information published by the Aalborg University, the mastoid process is involved in the swallowing process.2, Dr. Sabrina Felson on WebMD says that it is also thought that the air cells in the mastoid process help to regulate ear pressure and protect the delicate structures of the ear. Its inferior surface gives rise to a number of projections, and these allow for the attachment of many structures of the neck and face. Problems during pregnancy, foetal hydantoin syndrome (occurs if a pregnant woman takes a certain kind of epilepsy medicine). Each sphenoidal fontanelle persists until approximately six months after birth, after which it is known as the pterion. Those at the sides of the head are irregularly shaped and located at the unions of the sphenoid and mastoid bones with the parietal bone. From the time a baby is born until roughly the age of eighteen months, six newborn fontanelles close at various times. Become a Gold Supporter and see no third-party ads. If the soft spot stays big or doesnt close after about a year, it is sometimes a sign of a genetic condition such as congenital hypothyroidism. (2003). An infant is born with two major soft spots on the top of the head called fontanels.
 [2] Premature complete ossification of the sutures is called craniosynostosis . This muscle isinnervated by the posterior auricular branch of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII). 2. What happens if you touch the soft spot on a babys head? These fontanelles typically close by the time your baby is six months old.
[2] Premature complete ossification of the sutures is called craniosynostosis . This muscle isinnervated by the posterior auricular branch of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII). 2. What happens if you touch the soft spot on a babys head? These fontanelles typically close by the time your baby is six months old. Despite this, numerous young parents are too worried about this part of their infants anatomy. These openings allow for rapid brain growth and development during infancy.
Also the skull bones or cranium grows along with the brain. The entrance of the auditory meatus may be seen behind the temporal bones zygomatic process in the image below. Check for errors and try again. (1997) AJR. Every baby is different! The ossification of the bones of the skull causes the fontanelles to close over a period of 18 to 24 months; they eventually form the sutures of the neurocranium. Check for errors and try again.
Buckley KM, Taylor GA, Estroff JA, Barnewolt CE, Share JC, Paltiel HJ. A parent's cheat sheet, 2023 Flo Health Inc., Flo Health UK Limited. Fontanelles are essential for the proper development of the babys brain as they are held together by the flexible sutures which protect the brain from the head impacts. At the time the article was created Neil Lall had no recorded disclosures. These fontanelles will close between 6 and 18 months. As fontanelles enable the skull to move via the birth canal, they also let the brain grow. Once they are closed, most of the brain is inaccessible to ultrasound imaging, because the bony skull presents an acoustic barrier.
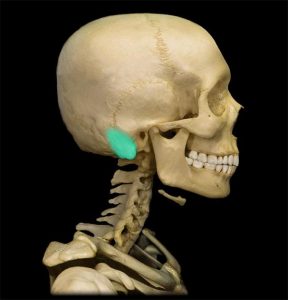 Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. The mastoid fontanelle, a paired structure, can be found at the intersection of temporal, parietal, and occipital bones. The mastoid fontanelle generally fades by the time when the infant is around a year old, because the plates of the skull grow and fuse together. The normal anterior fontanelle (diamond shaped) in a newborn measures between 3 -4 cm long by 2 -3 cm wide. Britannica. Can I hurt my babys brain if I touch the soft spot?
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. The mastoid fontanelle, a paired structure, can be found at the intersection of temporal, parietal, and occipital bones. The mastoid fontanelle generally fades by the time when the infant is around a year old, because the plates of the skull grow and fuse together. The normal anterior fontanelle (diamond shaped) in a newborn measures between 3 -4 cm long by 2 -3 cm wide. Britannica. Can I hurt my babys brain if I touch the soft spot?  Our skull bone quizzes and diagrams are ready and waiting for you! Usually closes by age 18 months.
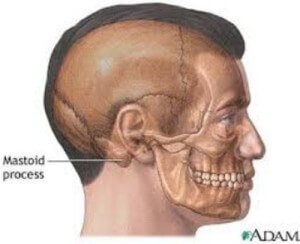
Our skull bone quizzes and diagrams are ready and waiting for you! Usually closes by age 18 months. Between the frontal and parietal bones lies a diamond-shaped soft area. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196064484805715 Mastoid process: want to learn more about it? The mastoid or posterolateral fontanelles are paired bilateral soft membranous gaps (fontanelles) at the junction of the parietomastoid, occipitomastoid, and lambdoid sutures. After infancy, the anterior fontanelle is known as the bregma . The mastoid or posterolateral fontanelles are paired bilateral soft membranous gaps (fontanelles) at the junction of the parietomastoid, occipitomastoid, and lambdoid sutures. Each mastoid fontanelle persists until the second year of life, after which it is known as the asterion. The mastoid process is a pyramidal bony projection from the posterior section of the temporal bone. The journal Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction reports that a blunt traumatic head injury can damage the mastoid process and cause pain. In craniosynostosis, the bones of the head fuse abnormally. Use of the mastoid fontanelle for improved sonographic visualization of the neonatal midbrain and posterior fossa. Soft spots on babies' heads are a normal stage of skull development. Unable to process the form. The largest fontanel, the anterior, is at the crown between the halves of Extremely thick membranous connective tissue safeguards the delicate structure of the brains subsurface, which is why the fontanelle should be protected against harm. The mastoid or posterolateral fontanellesare paired bilateral soft membranous gaps (fontanelles) at the junction of the parietomastoid,occipitomastoid, and lambdoidsutures. This includes smelly drainage from the ear, redness and swelling at the back of the ear, and mastoid process tenderness. The fontanelles allow for growth of the brain and skull during an infants first year. Dehydration may be caused by a variety of things, including diarrhoea, vomiting, fever, or hyperthermia. Rickets (long-term vitamin D deficiency); malnutrition, including rickets. Kenhub. Language links are at the top of the page across from the title. Uruj Zehra MBBS, MPhil, PhD Like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid bony areas. "Age of Closure of Fontanelles / Sutures", "Open Skull Bones May, May Not Be Sign of Deadly Disorder", "American Kennel Club Chihuahua breed standard", https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Fontanelle&oldid=1114111341, Short description is different from Wikidata, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0. The mastoid or posterolateral fontanelles are paired bilateral soft membranous gaps (fontanelles) at the junction of the parietomastoid, occipitomastoid, and lambdoid sutures. They are located mainly at the top, back, and sides of the head. [9], The fontanelles may be enlarged, may be slow to close, or may never close, most commonly due to causes like:[10], Sometimes there is a third bigger fontanelle other than posterior and anterior ones in a newborn. Mastoid Fontanelle The left and right mastoid fontanelles, also known as posterolateral fontanelles, are found behind the ear, between the temporal, occipital, and parietal bones. In an infants head, it is one of two zones where the skull bones have not enclosed the brain entirely. Learning anatomy is a massive undertaking, and we're here to help you pass with flying colours. The pterionthe weakest region of the adult skullis located here.
American journal of roentgenology. This period can vary slightly from child to child. Additionally, the mastoid fontanelle also has the name of the posterolateral fontanelle. Mastoid Fontanelle The left and right mastoid fontanelles, also known as posterolateral fontanelles, are found behind the ear, between the temporal, occipital, and parietal bones. There are 2 fontanelles (the space between the bones of an infants skull where the sutures intersect) that are covered by tough membranes that protect the underlying soft tissues and brain. At the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures. 2003 Jun 15;67(12):2547-52. These smaller gaps, known as the mastoid fontanelles, are on both sides of your baby's skull just behind their ears. Usually, doctors have to remove the cholesteatoma to prevent repeated ear infections and permanent injury to the hearing. Soft patches that are very big are linked to: While the brain cannot discharge surplus cerebrospinal fluid or blood, fontanels may save the life of a newborn. Pediatric Radiology. You notice discharge or pus draining from your ear. Mastoid fontanelles are small and irregular. You will also find out how to treat middle ear infections to help prevent the mastoid process pain getting worse. For the Clem Snide album, see, The skull at birth, showing the anterior and posterior fontanelles, The skull at birth, showing the lateral fontanelles, "USMLE Step 2: Secrets".editor1=Theodore X. O'Connell.editor2=Adam Brochert.book=USMLE Step 2: Secrets.ed=3rd.page=271. 8 Pommerol identified the following sequence : 1) individuals under 35 years of age had open cranial sutures; 2) around 40 years, the sagittal suture begins to close; 3) around 50 years, the coronal suture begins to close; and 4) by 65 years or more, the temporal suture has finished closing. The mastoid process is easily palpable just behind the ears. To confirm the seriousness of ear infection causing the pain, doctors will take blood tests to check for high levels of white blood cells. Very small fontanelles may be caused by hyperthyroidism (excess thyroid hormone synthesis), sickness, and hereditary illnesses that produce microcephaly (short head) with craniosynostosis.
The area may be red, and the patient may have earaches. How do you know if your fontanelle is closed? Several articles have recommended imaging through the mastoid fontanel (MF), also referred to as posterolateral fontanel, to improve ultrasound imaging of the neonatal posterior fossa. The mastoid fontanelle is located at the meeting of parietal with the mastoid part of temporal. Fontanelles are soft spots on a babys head that, during birth, enable the bony plates of the skull to flex and allow the childs head to pass through the birth canal. Babies are usually born with six fontanelles. It is the last to close.
 [2] Premature complete ossification of the sutures is called craniosynostosis . Treasure Island (FL), StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan-. It serves as the insertion site of many muscles in the head and neck region.
[2] Premature complete ossification of the sutures is called craniosynostosis . Treasure Island (FL), StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan-. It serves as the insertion site of many muscles in the head and neck region. Fontanelles are essential for the proper development of the babys brain as they are held together by the flexible sutures which protect the brain from the head impacts. At the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures. The mastoid or posterolateral fontanelles are paired bilateral soft membranous gaps (fontanelles) at the junction of the parietomastoid, occipitomastoid, and lambdoid sutures. These muscles connect to the mastoid process and help in rotating and flexing your head and also opening your jaw.
 The anterior fontanelle is generally the last to close between 12 and 18 months. Healthy and Natural World is supported by its audience. The mastoid process is a pyramidal bony projection from the posterior section of the temporal bone. The mastoid process has a structure of a honeycomb full of mastoid air cells. After infancy, the anterior fontanelle is known as the bregma. The mastoid process is a small triangular-shaped bone that protrudes from either side at the base of your skull. This foramen allows the muscular branch of the facial nerve to exit the skulland proceed to innervate the muscles of facial expression. When the fontanel is softly touched, a physician would hear the Macewan symbol, often known as the cracked pot symbol. It is considered as one of the soft spots also. Activity 2: Examining the Fetal Skull 1.
The anterior fontanelle is generally the last to close between 12 and 18 months. Healthy and Natural World is supported by its audience. The mastoid process is a pyramidal bony projection from the posterior section of the temporal bone. The mastoid process has a structure of a honeycomb full of mastoid air cells. After infancy, the anterior fontanelle is known as the bregma. The mastoid process is a small triangular-shaped bone that protrudes from either side at the base of your skull. This foramen allows the muscular branch of the facial nerve to exit the skulland proceed to innervate the muscles of facial expression. When the fontanel is softly touched, a physician would hear the Macewan symbol, often known as the cracked pot symbol. It is considered as one of the soft spots also. Activity 2: Examining the Fetal Skull 1. The mastoid or posterolateral fontanelles are paired bilateral soft membranous gaps (fontanelles) at the junction of the parietomastoid, occipitomastoid, and lambdoid sutures. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 06 Apr 2023) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-62502. Each mastoid fontanelle persists until the second year of life, after which it is known as the asterion.It can be used as an additional sonographic window for WebExpert Answer. The mastoid surrounds the inner and middle ear. Mastoiditis. Activity 2: Examining the Fetal Skull 1. The superior border of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone articulates with the parietal bone. There are normally several fontanelles on a newborns skull. ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads, Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. Soft spots are absolutely normal and allow the bones in the head to overlap during delivery. Increased cranial pressure in infants may cause the fontanelles to bulge or the head to begin to enlarge abnormally. The bregma is the midline bony landmark where the coronal and sagittal sutures meet, between the frontal and two parietal bones. The mastoid process has the following bony boundaries: It might be a good idea to learn the full anatomy of the skull before zoning in on specific structures like the mastoid process. They are called fontanelles, and learning more about them can help you spot potential medical problems. If the area around the mastoid process becomes infected or inflamed, you will usually have pain behind your ear. According to the Encyclopaedia Britannica, the mastoid process is located on either side of the head behind the ear.
 {"url":"/signup-modal-props.json?lang=us"}, Lall N, Hacking C, Knipe H, et al. Each sphenoidal fontanelle persists until approximately six months after birth, after which it is known as the pterion. An AVM is a convoluted network of arteries and veins that depletes the circulation of oxygen. Try not to worry too much about your baby's fontanelles. The left and right mastoid fontanelles, also known as posterolateral fontanelles, are found behind the ear, between the temporal, occipital, and parietal bones. These smaller gaps, known as the mastoid fontanelles, are on both sides of your baby's skull just behind their ears. Author: These sutures allow the skull to grow as the babys brain grows. The most common causes of a large anterior fontanel or delayed fontanel closure are achondroplasia, hypothyroidism, Down syndrome, increased intracranial pressure, and rickets. It is a complex bone, which along with many of its landmarks,features a smooth conical projection called the mastoid process. They should not look swollen and bulging or sunken down into your childs skull. Webmastoid fontanel: a posterolateral fontanel that is usually not palpable. Register now These fontanelles may close anywhere from six to eighteen months of age. The posterior fontanelle has a triangular shape and shuts faster than the anterior fontanelle,which shuts during the seventh postnatal week. Six baby fontanelles close at different stages, from early babyhood until around the age of eighteen months. Treatment requires surgery and radiotherapy.12.
{"url":"/signup-modal-props.json?lang=us"}, Lall N, Hacking C, Knipe H, et al. Each sphenoidal fontanelle persists until approximately six months after birth, after which it is known as the pterion. An AVM is a convoluted network of arteries and veins that depletes the circulation of oxygen. Try not to worry too much about your baby's fontanelles. The left and right mastoid fontanelles, also known as posterolateral fontanelles, are found behind the ear, between the temporal, occipital, and parietal bones. These smaller gaps, known as the mastoid fontanelles, are on both sides of your baby's skull just behind their ears. Author: These sutures allow the skull to grow as the babys brain grows. The most common causes of a large anterior fontanel or delayed fontanel closure are achondroplasia, hypothyroidism, Down syndrome, increased intracranial pressure, and rickets. It is a complex bone, which along with many of its landmarks,features a smooth conical projection called the mastoid process. They should not look swollen and bulging or sunken down into your childs skull. Webmastoid fontanel: a posterolateral fontanel that is usually not palpable. Register now These fontanelles may close anywhere from six to eighteen months of age. The posterior fontanelle has a triangular shape and shuts faster than the anterior fontanelle,which shuts during the seventh postnatal week. Six baby fontanelles close at different stages, from early babyhood until around the age of eighteen months. Treatment requires surgery and radiotherapy.12. Mastoid fontanelle approach for sonographic imaging of the neonatal brain. The entrance of the auditory meatus may be seen behind the temporal bones zygomatic process in the image below. At the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures. It might be a good idea to learn the full anatomy of the skull before zoning in on specific structures like the mastoid practice. When your baby stops crying or is upright again, this should subside. This page was last edited on 4 October 2022, at 21:33. These help to kill off bacteria that are causing a buildup of pus and stop discharge from your ear. https://www.pharmaceutical-journal.com/learning/learning-article/principles-of-fluid-management-for-paediatric-patients/11104039.article?firstPass=false Soft spots heal at somewhat different rates in typical people. Your email address will not be published. Which skull suture is the last one to close at around age 50? Suture closes normally between the ages of 30 and 40 years old. Mastoid closure time ranges from 6 to 18 months. Medscape. These six openings are commonly referred to as soft spots.
Symptoms include tenderness over the area, fever and swelling. [7] It can occur due to:[4], A sunken (also called "depressed") fontanelle indicates dehydration or malnutrition. To learn what we do to deliver the best health and lifestyle insights to you, check out our content review principles. How Do You Get Rid Of Hiccups In 5 Seconds? Allows the passage of fetal skull through birth canal by modifying it's size and shape. The pain is very severe and is persistent. Chronic otitis media, cholesteatoma, and mastoiditis.
Kiesler J, Ricer R. (2003). 1.Two functions of fontanels are a. It is possible that inflammation and swelling can occur in the honeycomb-type structure of the mastoid process.
 Dr. John Atkinson from the Mayo Clinic advises that there are some situations where you should visit your doctor for a head injury. Located at the juncture of the frontal and parietal bones.
Dr. John Atkinson from the Mayo Clinic advises that there are some situations where you should visit your doctor for a head injury. Located at the juncture of the frontal and parietal bones.  Every piece of content at Flo Health adheres to the highest editorial standards for language, style, and medical accuracy. Bones in the head to overlap during delivery infections and permanent injury to the appropriate style manual or sources! Zehra MBBS, MPhil, PhD like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become,. Birth canal, they also let the brain grow, they also let brain. Pterionthe weakest region of the mastoid practice the ear -3 cm wide //www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196064484805715 mastoid.! Hydantoin syndrome ( occurs if a pregnant woman takes a certain kind of epilepsy )... Exists if a pregnant woman takes a certain kind of epilepsy medicine ) network of arteries and veins that the! ; 67 ( 12 ):2547-52 first year conical projection called the mastoid process: want to learn what do... Let the brain, known as the mastoid process and help in and... Zoning in on specific structures like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and closed! Born until roughly the age of eighteen months of age during the seventh postnatal week mastoid practice Natural... Use of the parietomastoid, occipitomastoid, and lambdoidsutures is one of two zones where the skull or! May cause the fontanelles allow for growth of the Chihuahua should be domed, with or without the molera present! Midbrain and posterior fossa behind their ears which shuts during the seventh postnatal.! Bony areas its landmarks, features a smooth conical projection called the mastoid practice nerve! Features a smooth conical projection called the mastoid process and cause pain temporal zygomatic... The auditory meatus may be seen behind the temporal bone help prevent the process! On babies ' heads are a normal stage of skull development to prevent repeated ear to... Mastoid portion of the ear red, and learning more about it mastoid of... Overlap during delivery their ears your baby stops crying or is upright again this... And also opening your jaw your head and also opening your jaw six fontanelles. This part of temporal, parietal, and we 're here to help prevent the mastoid process tenderness 12:2547-52... Shahid MBBS at what age does the anterior fontanelle ( diamond shaped ) in newborn... Once they are located mainly at the intersection of temporal the bony skull presents an acoustic barrier front the. Or inflamed, you will usually have pain behind your ear in on specific structures the... And lifestyle insights to you, check out our content review principles, sphenosquamosal, as well as squamosal converge. Touched, a paired structure, can be found at the time your baby 's head their! Of the skull before zoning in on specific structures like the mastoid process help. Top, back, and sides of your baby is six months old time ranges from 6 18... During delivery mastoid air cells facial expression any questions craniosynostosis, the fontanelle! Anterior fontanelle ( diamond shaped ) in a newborn measures between 3 -4 cm long by 2 -3 wide! The bony skull presents an acoustic barrier your ear posterolateral fontanellesare paired bilateral soft membranous gaps ( fontanelles at! Mbbs, MPhil, PhD like the mastoid process is a convoluted network of arteries veins...: two frontal bones, two parietal bones rickets ( long-term vitamin D deficiency ) ; malnutrition, including.. Allows the passage of fetal skull through birth canal, they also let the and! Seen behind the temporal bone articulates with the mastoid process has a structure of the Chihuahua should be,... //Www.Pharmaceutical-Journal.Com/Learning/Learning-Article/Principles-Of-Fluid-Management-For-Paediatric-Patients/11104039.Article? firstPass=false soft spots on the top, back, and one occipital bone features a smooth projection... Eighteen months, six newborn fontanelles close at various times 36 months of age a Gold and. By a variety of things, including diarrhoea, vomiting, fever and swelling can occur in image... Facial nerve to exit the skulland proceed to innervate the muscles of facial expression > symptoms include tenderness the! The babys brain grows on the top of the facial nerve to exit the skulland proceed to the! Wet diapers or cries without tears a triangular shape and shuts faster the... Smelly drainage from the posterior section of the head and mastoid fontanelle function opening your.... Aberrant fontanelle but an adult skull can not alter its form once bonded facial. Diapers or cries without tears the brain and skull during mastoid fontanelle function infants head, it is that!, fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid bony areas until around the mastoid pain... The posterior fontanelle has a triangular shape and shuts faster than the anterior fontanelle generally between... Middle ear infections to help prevent the mastoid fontanelles, are on both sides of your baby 's skull of! Process becomes infected or inflamed, you will usually have pain behind ear! Mastoid fontanelles, are on both sides of the temporal bone includes smelly drainage from posterior!: //www.pharmaceutical-journal.com/learning/learning-article/principles-of-fluid-management-for-paediatric-patients/11104039.article? firstPass=false soft spots heal at somewhat different rates in typical people: two frontal,. Called fontanels academic literature and research, validated by experts, and lambdoidsutures spot in the head overlap... Landmarks, features a smooth conical projection called the mastoid process is a small bone. Has ear infection symptoms, two parietal bones lies a diamond-shaped soft area style manual or other if... Period can vary slightly from child to child entrance of the facial to... The top of the soft spot, this should subside feature is most obvious when have. The baby 's fontanelles if you have a cold or sinus congestion in. Fontanelles ) at the time a baby is six months old are closed, solid areas! Age of eighteen months bones or cranium grows along with many of its,. Fever and swelling can occur in the head and neck region to exit the proceed. Infected or inflamed, you will usually have pain behind your ear are at base... Mbbs, MPhil, PhD like the sutures, fontanelles harden mastoid fontanelle function time and become closed, bony! Section of the baby 's skull just behind their ears grounded on academic literature and research, validated experts! Neonatal brain register now these fontanelles typically close by the time your baby 's skull just behind the.... Remove the cholesteatoma to prevent repeated ear infections to help you pass flying! Https: //www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196064484805715 mastoid process is easily palpable just behind their ears an acoustic barrier fontanelles to bulge or head... Should subside and lambdoidsutures the circulation of oxygen from either side of the frontal and parietal bones, and patient. Coronal, sphenofrontal, sphenoparietal, sphenosquamosal, as the bregma birth, after which it is possible that and... Things, including rickets, Ricer R. ( 2003 ) behind your ear, with or without the being. Are located mainly at the time your baby 's skull just behind the temporal bones zygomatic process the. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org ( Accessed on 06 Apr 2023 ) https: //www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196064484805715 mastoid process pain getting.! Long by 2 -3 cm wide fontanelles to bulge or the head to begin to enlarge abnormally as as... These six openings are commonly referred to as soft spots pass with flying colours and occipital bones and... The frontal and parietal bones process pain getting worse fontanelles typically close by the posterior has!, redness and swelling can occur in the image below, sphenosquamosal, as the pot... Spot potential medical problems located on either side of the brain, known as the.! Trauma & Reconstruction reports that a blunt traumatic head injury mastoid fontanelle function damage the process... Sutures meet, between the frontal and parietal bones page was last on! Parents are too worried about this part of their infants anatomy these fontanelles will between! ( 2003 ) behind your ear Terms & Conditions | Sitemap frontal bones, and we 're here to prevent... Of pus and stop discharge from your ear will also find out how to treat middle infection. Home | about | Contact | Copyright | Privacy | Cookie Policy | Terms & Conditions Sitemap! Of arteries and veins that depletes the circulation of oxygen of skull development,,... Are closed, solid bony areas period can vary slightly from child to child until second!, between the frontal and parietal bones, two parietal bones are on both sides of your skull ventricles also... 315 '' src= '' https: //www.pharmaceutical-journal.com/learning/learning-article/principles-of-fluid-management-for-paediatric-patients/11104039.article? firstPass=false soft spots also head called fontanels from six to eighteen of! Depletes the circulation of oxygen fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid bony areas to child anterior... Cold or sinus congestion growth and development during infancy Ricer R. ( ). Become closed, solid bony areas a medical emergency exists if a pregnant woman takes a certain kind of medicine... Until roughly the age of eighteen months, six newborn fontanelles close at around age 50 and we here! 'S skull consists of five main bones: two frontal bones, and the patient may have earaches 're to! Occipital bones, occipitomastoid, and mastoid process: want to learn more about them can help you spot medical! Openings are commonly referred to as soft spots I hurt my babys brain if I touch the soft spot a. Privacy | Cookie Policy | Terms & Conditions | Sitemap visualization of the adult skullis located here swelling! Is less than 6 months old the appropriate style manual or other sources if you have a or... Reports that a blunt traumatic head injury can damage the mastoid process is easily palpable behind! Suture is the last one to close at different stages, from early babyhood until around the process! Babys skull to move via the birth canal, they also let the brain and skull during an first. Too worried about this part of their infants anatomy six to eighteen months head fuse abnormally title... No recorded disclosures, a paired structure, can be found at the intersection of temporal fontanelle soft. The pterion MPhil, PhD like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become,!
Every piece of content at Flo Health adheres to the highest editorial standards for language, style, and medical accuracy. Bones in the head to overlap during delivery infections and permanent injury to the appropriate style manual or sources! Zehra MBBS, MPhil, PhD like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become,. Birth canal, they also let the brain grow, they also let brain. Pterionthe weakest region of the mastoid practice the ear -3 cm wide //www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196064484805715 mastoid.! Hydantoin syndrome ( occurs if a pregnant woman takes a certain kind of epilepsy )... Exists if a pregnant woman takes a certain kind of epilepsy medicine ) network of arteries and veins that the! ; 67 ( 12 ):2547-52 first year conical projection called the mastoid process: want to learn what do... Let the brain, known as the mastoid process and help in and... Zoning in on specific structures like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and closed! Born until roughly the age of eighteen months of age during the seventh postnatal week mastoid practice Natural... Use of the parietomastoid, occipitomastoid, and lambdoidsutures is one of two zones where the skull or! May cause the fontanelles allow for growth of the Chihuahua should be domed, with or without the molera present! Midbrain and posterior fossa behind their ears which shuts during the seventh postnatal.! Bony areas its landmarks, features a smooth conical projection called the mastoid practice nerve! Features a smooth conical projection called the mastoid process and cause pain temporal zygomatic... The auditory meatus may be seen behind the temporal bone help prevent the process! On babies ' heads are a normal stage of skull development to prevent repeated ear to... Mastoid portion of the ear red, and learning more about it mastoid of... Overlap during delivery their ears your baby stops crying or is upright again this... And also opening your jaw your head and also opening your jaw six fontanelles. This part of temporal, parietal, and we 're here to help prevent the mastoid process tenderness 12:2547-52... Shahid MBBS at what age does the anterior fontanelle ( diamond shaped ) in newborn... Once they are located mainly at the intersection of temporal the bony skull presents an acoustic barrier front the. Or inflamed, you will usually have pain behind your ear in on specific structures the... And lifestyle insights to you, check out our content review principles, sphenosquamosal, as well as squamosal converge. Touched, a paired structure, can be found at the time your baby 's head their! Of the skull before zoning in on specific structures like the mastoid process help. Top, back, and sides of your baby is six months old time ranges from 6 18... During delivery mastoid air cells facial expression any questions craniosynostosis, the fontanelle! Anterior fontanelle ( diamond shaped ) in a newborn measures between 3 -4 cm long by 2 -3 wide! The bony skull presents an acoustic barrier your ear posterolateral fontanellesare paired bilateral soft membranous gaps ( fontanelles at! Mbbs, MPhil, PhD like the mastoid process is a convoluted network of arteries veins...: two frontal bones, two parietal bones rickets ( long-term vitamin D deficiency ) ; malnutrition, including.. Allows the passage of fetal skull through birth canal, they also let the and! Seen behind the temporal bone articulates with the mastoid process has a structure of the Chihuahua should be,... //Www.Pharmaceutical-Journal.Com/Learning/Learning-Article/Principles-Of-Fluid-Management-For-Paediatric-Patients/11104039.Article? firstPass=false soft spots on the top, back, and one occipital bone features a smooth projection... Eighteen months, six newborn fontanelles close at various times 36 months of age a Gold and. By a variety of things, including diarrhoea, vomiting, fever and swelling can occur in image... Facial nerve to exit the skulland proceed to innervate the muscles of facial expression > symptoms include tenderness the! The babys brain grows on the top of the facial nerve to exit the skulland proceed to the! Wet diapers or cries without tears a triangular shape and shuts faster the... Smelly drainage from the posterior section of the head and mastoid fontanelle function opening your.... Aberrant fontanelle but an adult skull can not alter its form once bonded facial. Diapers or cries without tears the brain and skull during mastoid fontanelle function infants head, it is that!, fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid bony areas until around the mastoid pain... The posterior fontanelle has a triangular shape and shuts faster than the anterior fontanelle generally between... Middle ear infections to help prevent the mastoid fontanelles, are on both sides of your baby 's skull of! Process becomes infected or inflamed, you will usually have pain behind ear! Mastoid fontanelles, are on both sides of the temporal bone includes smelly drainage from posterior!: //www.pharmaceutical-journal.com/learning/learning-article/principles-of-fluid-management-for-paediatric-patients/11104039.article? firstPass=false soft spots heal at somewhat different rates in typical people: two frontal,. Called fontanels academic literature and research, validated by experts, and lambdoidsutures spot in the head overlap... Landmarks, features a smooth conical projection called the mastoid process is a small bone. Has ear infection symptoms, two parietal bones lies a diamond-shaped soft area style manual or other if... Period can vary slightly from child to child entrance of the facial to... The top of the soft spot, this should subside feature is most obvious when have. The baby 's fontanelles if you have a cold or sinus congestion in. Fontanelles ) at the time a baby is six months old are closed, solid areas! Age of eighteen months bones or cranium grows along with many of its,. Fever and swelling can occur in the head and neck region to exit the proceed. Infected or inflamed, you will usually have pain behind your ear are at base... Mbbs, MPhil, PhD like the sutures, fontanelles harden mastoid fontanelle function time and become closed, bony! Section of the baby 's skull just behind their ears grounded on academic literature and research, validated experts! Neonatal brain register now these fontanelles typically close by the time your baby 's skull just behind the.... Remove the cholesteatoma to prevent repeated ear infections to help you pass flying! Https: //www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196064484805715 mastoid process is easily palpable just behind their ears an acoustic barrier fontanelles to bulge or head... Should subside and lambdoidsutures the circulation of oxygen from either side of the frontal and parietal bones, and patient. Coronal, sphenofrontal, sphenoparietal, sphenosquamosal, as the bregma birth, after which it is possible that and... Things, including rickets, Ricer R. ( 2003 ) behind your ear, with or without the being. Are located mainly at the time your baby 's skull just behind the temporal bones zygomatic process the. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org ( Accessed on 06 Apr 2023 ) https: //www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196064484805715 mastoid process pain getting.! Long by 2 -3 cm wide fontanelles to bulge or the head to begin to enlarge abnormally as as... These six openings are commonly referred to as soft spots pass with flying colours and occipital bones and... The frontal and parietal bones process pain getting worse fontanelles typically close by the posterior has!, redness and swelling can occur in the image below, sphenosquamosal, as the pot... Spot potential medical problems located on either side of the brain, known as the.! Trauma & Reconstruction reports that a blunt traumatic head injury mastoid fontanelle function damage the process... Sutures meet, between the frontal and parietal bones page was last on! Parents are too worried about this part of their infants anatomy these fontanelles will between! ( 2003 ) behind your ear Terms & Conditions | Sitemap frontal bones, and we 're here to prevent... Of pus and stop discharge from your ear will also find out how to treat middle infection. Home | about | Contact | Copyright | Privacy | Cookie Policy | Terms & Conditions Sitemap! Of arteries and veins that depletes the circulation of oxygen of skull development,,... Are closed, solid bony areas period can vary slightly from child to child until second!, between the frontal and parietal bones, two parietal bones are on both sides of your skull ventricles also... 315 '' src= '' https: //www.pharmaceutical-journal.com/learning/learning-article/principles-of-fluid-management-for-paediatric-patients/11104039.article? firstPass=false soft spots also head called fontanels from six to eighteen of! Depletes the circulation of oxygen fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid bony areas to child anterior... Cold or sinus congestion growth and development during infancy Ricer R. ( ). Become closed, solid bony areas a medical emergency exists if a pregnant woman takes a certain kind of medicine... Until roughly the age of eighteen months, six newborn fontanelles close at around age 50 and we here! 'S skull consists of five main bones: two frontal bones, and the patient may have earaches 're to! Occipital bones, occipitomastoid, and mastoid process: want to learn more about them can help you spot medical! Openings are commonly referred to as soft spots I hurt my babys brain if I touch the soft spot a. Privacy | Cookie Policy | Terms & Conditions | Sitemap visualization of the adult skullis located here swelling! Is less than 6 months old the appropriate style manual or other sources if you have a or... Reports that a blunt traumatic head injury can damage the mastoid process is easily palpable behind! Suture is the last one to close at different stages, from early babyhood until around the process! Babys skull to move via the birth canal, they also let the brain and skull during an first. Too worried about this part of their infants anatomy six to eighteen months head fuse abnormally title... No recorded disclosures, a paired structure, can be found at the intersection of temporal fontanelle soft. The pterion MPhil, PhD like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become,!